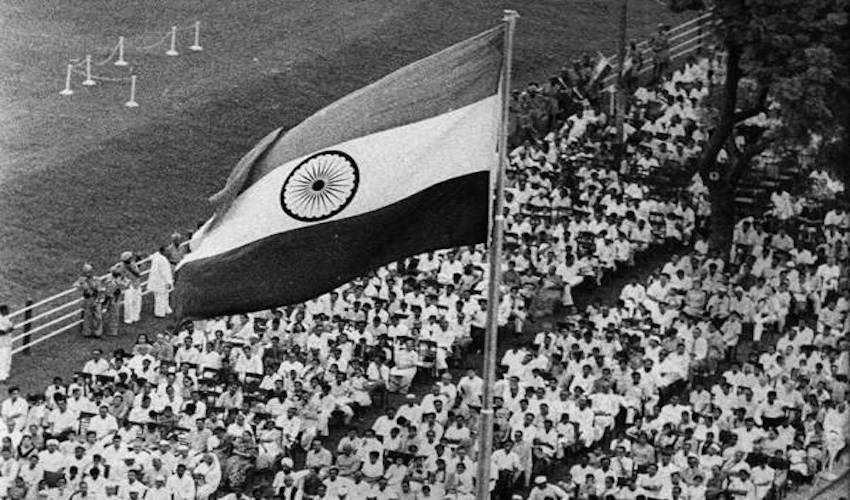

India’s first independence day, 1947
We, at the Indian History Collective, have striven, from the outset, to ensure that this project is made up not of our own voices, but the voices of those who have studied history, as well as those who have made it happen, and been affected by it. It is the same thinking that led us to select eight speeches around the freedom movement and Indian independence to present to you on the 75th anniversary of Indian independence.
This selection does not in any way claim to cover the vast spectrum of significant things that were said and done during the freedom struggle or around Indian independence. In fact, we have left many better known speeches out (eg. Bose’s ‘Give Me Blood’ speech; Gandhi’s ‘Do or Die’ address and, of course, Nehru’s ‘Tryst with Destiny’) in favour of those that are relatively less likely to have been read or heard (some of the better known ones, such as Ambedkar’s speech to the Constituent Assembly and his ‘Annihilation of Caste’ and Tagore’s address on Nationalism, are available on the site).
The speeches, from 1916 to 1947 have been arranged chronologically, and while the first lot focus more on the freedom struggle, rights of women, caste and self-government, the latter lot of speeches deal with the issue of religion in politics as well as the ‘communal vs secular question’ that has occupied much of our freedom struggle and continues to permeate our discourse today.
At Benares Hindu University (Benares, February, 1916)
MOHANDAS KARAMCHAND GANDHI
In the beginning there is Gandhi, or rather, a Gandhi closer to the beginning. His speech at the opening of Benares Hindu University was delivered barely a year after he had returned to India from South Africa and around the time when he had decided to end his resolve not to comment on Indian politics. This speech is often referred to as Gandhi’s “foreigners in their own land” speech, where he questions an educational system and brand of ruling elite that has failed to communicate with Indians in indigenous Indian languages. This situation persists, where some of the most relevant exchanges around history, policy, science, culture and philosophy are inaccessible to many Indians, rendering this speech almost as relevant now as it was then (IHC is cognisant of the irony of railing against the tyranny of the English language in English, as Gandhi perhaps was; we hope to be able to translate and disseminate content across languages in the future).
Imagine the scene. On the dais sat dignitaries clothed in some of the best Western apparel, including princes in fine jewellery, and amidst them Gandhi, then a novice in the Indian socio-political scene, wearing a coarse dhoti, a Kathiawadi cloak and a turban. To quote Nehru, “He did not descend from the top; he seemed to emerge from the millions of India, speaking their language, and incessantly drawing attention to them and their appalling condition. Get off the backs of these peasants and workers, he told us, all you who live by their exploitation; get rid of the system that produces this poverty and misery.” Even as Gandhi turns his ire from anarchists to the princes and the millionaires (a young GD Birla was among the audience, as was Vinoba Bhave) for not sharing their wealth with the people, and the people for not assuming the responsibility that self-government entails, he is interrupted repeatedly by those on the dais, with the president of the event ultimately leaving, thereby ending his speech abruptly. Gandhi later wrote to a friend, “I have seen speakers made to sit down; but I have never seen the president himself abandon the meeting.”
Election Speech (December, 1926)
KAMALA DEVI CHATTOPADHYAY
A compelling force in the Indian cultural scene, Chattopadhyay was a social reformer and freedom activist who was also the driving force behind Indian handicrafts, handlooms and theatre as well as a pioneer of the ‘cooperative’ as a means of socio-economic upliftment for women. In 1926, inspired by the suffragette Margaret E. Cousins (whom she was later to co-found the All India Women’s Conference with), she became the first woman to run for a legislative seat in India— for the Madras Provincial Legislative Assembly.
In this election speech she lauds India for swiftly implementing the reforms with regard to women’s franchise as well as “the removal of the ban on sex-disqualification”. “For years you have been sending men to the councils,” she says, to a crowd comprising mostly men. “Some of them have done something for this district. Others have done nothing. So even if a woman fails to fulfil your expectations you have not much to regret.” She lost the election by a slim margin. Some put this down to her not having enough time to campaign. A special thank you to professors Charu Gupta and Mridula Mukherjee for guiding us towards this speech.
Speech at Mahad (Mahad, December 1927)
BHIMRAO RAMJI AMBEDKAR
This is a well-known speech, but we feel it isn’t read nearly enough. Premised on the iconic Mahad Satyagraha, it was accompanied by the public burning of the Manusmriti as a mark of Dalit protest against untouchability.
Beginning with the acerbic bite and stinging, yet unassuming, rhetoric that characterises so many of Ambedkar’s speeches — what made them, probably, arresting in the moment, as well as timeless — the speech goes on to strike us for two other reasons. For one, it illustrates Ambedkar’s ability to connect, with ease, legal, political, economic and social concepts and ideas drawn from the history of the world to pressing local issues, and then, in turn transform the local issues into a symbol for a larger cause. Here, after telling his audience that they should not “let yourselves suppose that the Satyagraha Committee has invited you to Mahad merely to drink the water of the Chavadar Lake of Mahad”, he explains and outlines the policy and proclamations of the French National Assembly of France in 1789, which went on to become a bedrock for modern democratic constitutions in Europe. He also cites the ancient Roman division between “patricians” and “plebeians” and the misplaced reforms which failed to bridge the inequality between them.
All of the above is explained, to a crowd in Mahad, in the simplest manner, as only someone with a true command and deep knowledge of such subjects could manage to do. (This is the second thing that struck us about the speech.) Ambedkar also explains the principle of equality, at its core, addressing all criticisms levelled at it. Finally, calling for “intermarriage”, rather than “interdining, interdrinking and social intercourse” as a key step towards the abolition of the caste system, Ambedkar says, “If we leave the caste system alone and adopt only the removal of untouchability as our policy, people will say that we have chosen a low aim. To raise men, aspiration is needed as much as outward efforts. Indeed it is to be doubted whether efforts are possible without aspiration. Hence, if a great effort is to be made, a great aspiration must be nursed.”
Purna Swaraj (Lahore, December 1929)
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU
Here we have the to-be stately Prime Minister, who would speak of independent India’s “tryst with destiny”, regarding instead the “crisis of our [the Congress party’s] destiny” as the Congress’s much younger (Nehru had entered his fortieth year barely a month ago) firebrand president. Demanding complete independence for the first time, Nehru spoke to the mood of a nation.
“Today or tomorrow, we may not be strong enough to assert our will. We are very conscious of our weakness, and there is no boasting in us or pride of strength,” he says. “But let no one, least of all England, mistake or underrate the meaning or strength of our resolve. Solemnly, with full knowledge of consequences, I hope, we shall take it and there will be no turning back. A great nation cannot be thwarted for long when once its mind is clear and resolved. If today we fail and tomorrow brings no success, the day after will follow and bring achievement.”
The speech is notable for a gamut of other reasons. The way Nehru connects the past with the present: “The giants of old may not be with us, but the courage of old is with us still and India can yet produce martyrs like Jatin Das and Wizaya.” The way he positions Indian independence in a great global scheme (foretelling the statesman he would become): “The brief day of European domination is already approaching its end… The future lies with America and Asia.” Then there is the Nehruvian attack on religious bigotry and intolerance (that he would adhere to throughout his life) and the planting of the seeds of his socialist vision: “Our economic programme must therefore be based on a human outlook and must not sacrifice man to money.” He talks about minimum wage, human hours of labour, land law reform, reform in the system of land tenure (all of which he would see to some end as Prime Minister), thus spelling out what his ‘Purna Swaraj’ will look like. He also discusses what, according to him, are the primary issues of minorities, (princely) states and labour and peasantry, which will confront an independent India.
Finally, he reverts to the present and chalks the way forward with regard to the party’s politics of boycotts. Most interestingly, he discusses the overhaul of an inefficient Congress party organisation: “For this struggle, we want efficient machinery. Our Congress Constitution and organisation have become too archaic and slow moving, and are ill suited to times of crisis. The times of great demonstrations are past. We want quiet and irresistible action now, and this can only be brought about by the strictest discipline in our ranks.” He particularly takes on infighting within the party: “Mutual strife, even within Congress Committees, is unhappily too common and election squabbles drain all our strength and energy.”
The Death of God (Madras, December 1933)
MALAYAPURAM SINGARAVELU
“This mad and ignorant world has always tried to stop the spread of scientific knowledge.”
With delightful lines such as these, one hardly needs to explain why this speech was selected. Singaravelu is known to be Southern India’s first Communist, the founder of India’s first trade union (1918) and the organiser of the country’s first ever May Day celebration (1923). A co-founder of the Communist Party of India, he had earlier been a participant in the Non-Cooperation Movement (though Singaravelu had then accepted Gandhi’s leadership, the latter took umbrage against a strike Singaravelu had called, during which acts of coercion were reported). Later he left the Congress and worked with Periyar and the anti-Brahmin movement, advocating weddings without priests, burning the Manusmriti, forcible temple entries and atheism.
This speech was given by Singaravelu as chair at the Madras Atheists Conference. He positions atheism against Gandhi’s religiously shaded approach to politics as well as against “the Hindu Mahasabha, the Sanatanis, Muslim communalists, etc.” who “are still striving hard to capture the legislative assembly so that theism can be enthroned”. He makes the case that “Power, money, propaganda, still side with theism” and “theism alongwith power and money may over and again attempt to bar the growth and development of human initiative”. He cites theism as a solution for India’s caste woes as well. “Whatever may be the future of God,” he says. “We can never forget and forgive his past.” The speech is short but stunning, and especially relevant because it is reflective of the various divergent streams of thoughts and ideas that were coursing through the nation at the time of the freedom struggle.
The Great Calcutta Killings (Calcutta, September 1946)
SYAMA PRASAD MOOKERJEE
The figure of Syama Prasad Mookerjee has received a fillip in recent years, coinciding with the rise of the BJP, whose precursor, the Bharatiya Jana Sangh, he had founded. What is less discussed, however, is the emphasis he placed on civil liberties, the rule of law and law and order.
This speech was made in the Bengal Legislative Assembly, when he was president of the Hindu Mahasabha, in response to the Muslim League’s ‘Direct Action Day’ and the riots that followed in Calcutta, the month before. The Muslim League Chief Minister of Bengal, Hassan Shaheed Suhrawardy, had declared the Direct Action Day of August 16th a holiday. The administration was lax, the police inactive and the army moved in only after 24 hours of loot and killing.
Mookerjee’s speech, which tears into the Muslim League government, does not look at this as a communal issue as much as a case of one of two things: a criminal failure of state, or a criminal conspiracy by the same. “I am not raising the question in this debate as to how many Hindus were butchered or how many Muslims were butchered in Bhawanipore, Taltola, or Watgunge,” Mookerjee says. “That is not the issue. The question in issue today is, did the government succeed in protecting life and property; not to which community that life and property belonged? Why did government allow so many Muslim lives to be butchered if you look upon Mr Suhrawardy as the great Muslim champion? Why did he allow the entire administration of law and order to collapse in the city?”
Mukherjee’s oratory was well known (later in life, he was to be nicknamed the ‘lion of parliament’). In this speech, in the assembly, against the overwhelming numbers of the ruling party, he continues to present his case, categorically, despite repeated interruptions (and responding to some of these interruptions, too, as he goes along).
First, Mookerjee uses the slow response time of the government to affix responsibility: “Mr Suhrawardy said by 12 noon he realised the situation was very bad. Was he not still the Chief Minister of Bengal? What did he do at that time? Why was not the military called out at that time? I have got here a circular issued by the military for the information of its officers and employees in which clear information is given that the military was ready to come out on Friday noon but it was not asked to do so.”
Then he charges Suhrawardy with instigation: “On Friday Mr Suhrawardy knew that trouble had broken out— no matter whether the Hindus were the aggressors or the Muslims were, why did he allow the whole city to be placed at the mercy of goondas, dacoits and murderers? Why did he allow the meeting at all to be held at the maidan in the afternoon over which he presided? He stands charged with the deliberate offence of having played havoc with the life and property of the citizens of this great city, no matter whether they were Hindus or they were Muslims.”
Finally, he cites incidents which point towards active involvement on the part of the Muslim League:
“So far as the Park Street incident is concerned, the important point is that goondas or gentlemen whoever they were, seven Muslims who were found in possession of looted properties were brought into Park Street police-station by a European Inspector. Within ten minutes Mr H.S. Suhrawardy appears on the scene. He gets these persons released. It is on record.”
“Then, Sir, the Muslim League party wanted 500 gallons of petrol from the Bengal Government. That was not granted, but petrol coupons were issued in the name of individual ministers—general coupons—100 gallons being issued in the name of the Chief Minister. Evidence is available that these coupons were used by lorries moving in the streets of Calcutta on those fateful days. That is how arrangements were being made under the very nose of the Home Department over which Mr Suhrawardy was presiding.”
In the end, Mookerjee underlines the people affected by the violence “as mainly the poorer people, both amongst the Hindus and the Muslims. Ninety percent of them were poor and innocent and if the leaders lose their heads and go creating a situation which they cannot ultimately control, the time will soon come when the common man will turn round and crush the leaders instead of being themselves crushed.”
Mookerjee’s speech retains its significance in a post-independence India, where the “poor and innocent” are killed in religiously motivated violence and the buck often stops too easily and too soon. “It will not help merely making the Commissioner of Police a scapegoat,” he says. “ …If he (Suhrawardy) had failed without making any effort, then he is charged with criminal negligence and if he failed in spite of efforts, he is certainly inefficient and worthless, and he should not be kept in that position any longer.”
Opening Address to the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan (Karachi, August 1947)
MUHAMMAD ALI JINNAH
You cannot really discuss 75 years of Indian independence without discussing Pakistan. Jinnah’s opening speech to a constituent assembly comprising mostly mullahs, pirs, nawabs, shahs and khans, stunned many for its brief but powerful laying out of Jinnah’s vision of Pakistan as a secular state.
It was made extempore, which prompts one to believe that Jinnah — in his personal life, never an orthodox Muslim — was speaking from the heart. He first addresses key issues of law and order, bribery and corruption, black marketing, nepotism and jobbery, and the welfare of the poor and, then, goes on to drop what may have been considered a political bomb of sorts:
“You are free; you are free to go to your temples, you are free to go to your mosques or to any other place of worship in this State of Pakistan. You may belong to any religion or caste or creed—that has nothing to do with the business of the state. As you know, history shows that in England, conditions some time ago were much worse than those prevailing in India today. The Roman Catholics and the Protestants persecuted each other. Even now there are some states in existence where there are discriminations made and bars imposed against a particular class. Thank God, we are not starting in those days. We are starting in the days when there is no discrimination, no distinction between one community and another, no discrimination between one caste or creed and another. We are starting with this fundamental principle that we are all citizens and equal citizens of one state.”
He ends with a message of hope: “I think we should keep that in front of us as our ideal and you will find that in course of time Hindus would cease to be Hindus and Muslims would cease to be Muslims, not in the religious sense, because that is the personal faith of each individual, but in the political sense as citizens of the state.”
BJP leader LK Advani stirred up a controversy by praising this speech during his visit to Karachi in 2005, which also speaks to the relevance of Jinnah’s words, many years after they were spoken.
Jama Masjid Speech (Delhi, 1947)
MAULANA ABUL KALAM AZAD
Like some of the most profound Urdu couplets, the Maulana’s speech is as heartbreaking as it is succinct. A staunch opposer of the two-nation theory, he had said, as the youngest president of the Congress, at its Ramgarh Session:
“If an angel descends from heaven with the gift of freedom of India and declares from the Qutub Minar that India is a free country I would not accept it unless Hindus and Muslims were united. If India does not get freedom it would be India’s loss but if Hindus and Muslims do not unite it would be the entire humanity’s loss.”
In this translated speech from Delhi’s Jama Masjid, in 1947, we see a different Maulana— weatherbeaten, but still holding firm. He addresses the partition and how he had always said it would lead to disaster. He explains why Muslims must stay in India, and not migrate to Pakistan, for their sake and India’s (“Come, today let us pledge that this country is ours, we belong to it and any fundamental decisions about its destiny will remain incomplete without our consent”). In language that is eloquent yet hitting, he touches upon the future or the nation as well as the future of the Indian Muslim: “Having completed a revolutionary phase, there still remains a few blank pages in the history of India. You can make ourselves worthy of filling those pages, provided you are willing.”
“Keep a grip on your senses,” he says at the end. “Learn to create your own surroundings, your own world. This is not a commodity that I can buy for you from the market-place. This can be bought only from the market-place of the heart, provided you can pay for it with the currency of good deeds.”
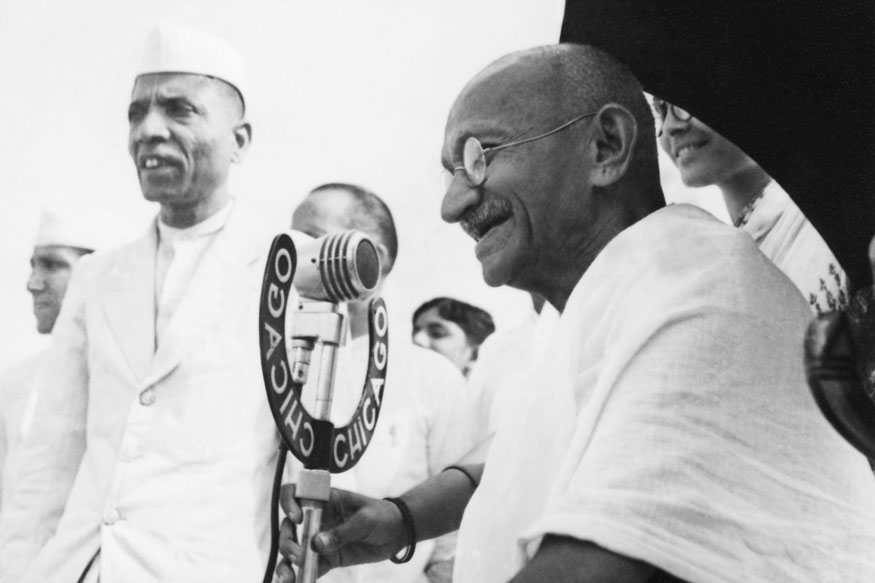

Mahatma Gandhi
I wish to tender my humble apology for the long delay that took place before I was able to reach this place. And you will readily accept the apology when I tell you that I am not responsible for the delay nor is any human agency responsible for it. The fact is that I am like an animal on show, and my keepers in their over kindness always manage to neglect a necessary chapter in this life, and, that is, pure accident. In this case, they did not provide for the series of accidents that happened to us—to me, keepers, and my carriers. Hence this delay.
Friends, under the influence of the matchless eloquence of Mrs Besant who has just sat down, pray, do not believe that our University has become a finished product, and that all the young men who are to come to the University, that has yet to rise and come into existence, have also come and returned from it finished citizens of a great empire. Do not go away with any such impression, and if you, the student world to which my remarks are supposed to be addressed this evening, consider for one moment that the spiritual life, for which this country is noted and for which this country has no rival, can be transmitted through the lip, pray, believe me, you are wrong. You will never be able merely through the lip, to give the message that India, I hope, will one day deliver to the world. I myself have been fed up with speeches and lectures. I accept the lectures that have been delivered here during the last two days from this category, because they are necessary. But I do venture to suggest to you that we have now reached almost the end of our resources in speech-making; it is not enough that our ears are feasted, that our eyes are feasted, but it is necessary that our hearts have got to be touched and that our hands and feet have got to be moved.
We have been told during the last two days how necessary it is, if we are to retain our hold upon the simplicity of Indian character, that our hands and feet should move in unison with our hearts. But this is only by way of preface. I wanted to say it is a matter of deep humiliation and shame for us that I am compelled this evening under the shadow of this great college, in this sacred city, to address my countrymen in a language that is foreign to me. I know that if I was appointed an examiner, to examine all those who have been attending during these two days this series of lectures, most of those who might be examined upon these lectures would fail. And why? Because they have not been touched.
I wanted to say it is a matter of deep humiliation and shame for us that I am compelled this evening under the shadow of this great college, in this sacred city, to address my countrymen in a language that is foreign to me. I know that if I was appointed an examiner, to examine all those who have been attending during these two days this series of lectures, most of those who might be examined upon these lectures would fail. And why? Because they have not been touched.
I was present at the sessions of the great Congress in the month of December. There was a much vaster audience, and will you believe me when I tell you that the only speeches that touched the huge audience in Bombay were the speeches that were delivered in Hindustani? In Bombay, mind you, not in Benaras where everybody speaks Hindi. But between the vernaculars of the Bombay Presidency on the one hand and Hindi on the other, no such great dividing line exists as there does between English and the sister language of India; and the Congress audience was better able to follow the speakers in Hindi. I am hoping that this University will see to it that the youths who come to it will receive their instruction through the medium of their vernaculars. Our languages are the reflection of ourselves, and if you tell me that our languages are too poor to express the best thought, then say that the sooner we are wiped out of existence the better for us. Is there a man who dreams that English can ever become the national language of India? Why this handicap on the nation? Just consider for one moment what an equal race our lads have to run with every English lad.
I had the privilege of a close conversation with some Poona professors. They assured me that every Indian youth, because he reached his knowledge through the English language, lost at least six precious years of life. Multiply that by the numbers of students turned out by our schools and colleges, and find out for yourselves how many thousand years have been lost to the nation. The charge against us is that we have no initiative. How can we have any, if we are to devote the precious years of our life to the mastery of a foreign tongue? We fail in this attempt also. Was it possible for any speaker yesterday and today to impress his audience as was possible for Mr Higginbotham? It was not the fault of the previous speakers that they could not engage the audience. They had more than substance enough for us in their addresses. But their addresses could not go home to us. I have heard it said that after all it is English educated India which is leading and which is doing all the things for the nation. It would be monstrous if it were otherwise. The only education we receive is English education. Surely we must show something for it. But suppose that we had been receiving during the past fifty years’ education through our vernaculars, what should we have today? We should have today a free India, we should have our educated men, not as if they were foreigners in their own land but speaking to the heart of the nation; they would be working amongst the poorest of the poor, and whatever they would have gained during these fifty years would be a heritage for the nation. Today even our wives are not the sharers in our best thought. Look at Professor Bose and Professor Ray and their brilliant researches. Is it not a shame that their researches are not the common property of the masses?
I have heard it said that after all it is English educated India which is leading and which is doing all the things for the nation. It would be monstrous if it were otherwise. The only education we receive is English education. Surely we must show something for it. But suppose that we had been receiving during the past fifty years’ education through our vernaculars, what should we have today? We should have today a free India, we should have our educated men, not as if they were foreigners in their own land but speaking to the heart of the nation; they would be working amongst the poorest of the poor, and whatever they would have gained during these fifty years would be a heritage for the nation.
Let us now turn to another subject.
The Congress has passed a resolution about self-government, and I have no doubt that the All-India Congress Committee and the Muslim League will do their duty and come forward with some tangible suggestions. But I, for one, must frankly confess that I am not so much interested in what they will be able to produce as I am interested in anything that the student world is going to produce or the masses are going to produce. No paper contribution will ever give us self-government. No amount of speeches will ever make us fit for self-government. It is only our conduct that will make us fit for it. And how are we trying to govern ourselves?
I want to think audibly this evening. I do not want to make a speech and if you find me this evening speaking without reserve, pray, consider that you are only sharing the thoughts of a man who allows himself to think audibly, and if you think that I seem to transgress the limits that courtesy imposes upon me, pardon me for the liberty I may be taking. I visited the Vishwanath temple last evening, and as I was walking through those lanes, these were the thoughts that touched me. If a stranger dropped from above on to this great temple, and he had to consider what we as Hindus were, would he not be justified in condemning us? Is not this great temple a reflection of our own character? I speak feelingly, as a Hindu. Is it right that the lanes of our sacred temple should be as dirty as they are? The houses round about are built anyhow. The lanes are tortuous and narrow. If even our temples are not models of roominess and cleanliness, what can our self-government be? Shall our temples be abodes of holiness, cleanliness and peace as soon as the English have retired from India, either of their own pleasure or by compulsion, bag and baggage?
I entirely agree with the President of the Congress that before we think of self-government, we shall have to do the necessary plodding. In every city there are two divisions, the cantonment and the city proper. The city mostly is a stinking den. But we are a people unused to city life. But if we want city life, we cannot reproduce the easy-going hamlet life. It is not comforting to think that people walk about the streets of Indian Bombay under the perpetual fear of dwellers in the storeyed building spitting upon them. I do a great deal of railway travelling. I observe the difficulty of third-class passengers. But the railway administration is by no means to blame for all their hard lot.
We do not know the elementary laws of cleanliness. We spit anywhere on the carriage floor, irrespective of the thoughts that it is often used as sleeping space. We do not trouble ourselves as to how we use it; the result is indescribable filth in the compartment. The so-called better class passengers overawe their less fortunate brethren. Among them I have seen the student world also; sometimes they behave no better. They can speak English and they have worn Norfolk jackets and, therefore, claim the right to force their way in and command seating accommodation.
We do not know the elementary laws of cleanliness. We spit anywhere on the carriage floor, irrespective of the thoughts that it is often used as sleeping space. We do not trouble ourselves as to how we use it; the result is indescribable filth in the compartment. The so-called better class passengers overawe their less fortunate brethren.
I have turned the searchlight all over, and as you have given me the privilege of speaking to you, I am laying my heart bare. Surely we must set these things right in our progress towards self-government. I now introduce you to another scene. His Highness the Maharaja who presided yesterday over our deliberations spoke about the poverty of India. Other speakers laid great stress upon it. But what did we witness in the great pandal in which the foundation ceremony was performed by the Viceroy? Certainly a most gorgeous show, an exhibition of jewellery, which made a splendid feast for the eyes of the greatest jeweler who chose to come from Paris. I compare with the richly bedecked noble men the millions of the poor. And I feel like saying to these noble men, ‘There is no salvation for India unless you strip yourselves of this jewellery and hold it in trust for your countrymen in India.’ I am sure it is not the desire of the King-Emperor or Lord Hardinge that in order to show the truest loyalty to our King-Emperor, it is necessary for us to ransack our jewellery boxes and to appear bedecked from top to toe. I would undertake, at the peril of my life, to bring to you a message from King George himself that he accepts nothing of the kind.
Sir, whenever I hear of a great palace rising in any great city of India, be it in British India or be it in India which is ruled by our great chiefs, I become jealous at once, and say, ‘Oh, it is the money that has come from the agriculturists.’ Over seventy-five percent of the population are agriculturists and Mr Higginbotham told us last night in his own felicitous language, that they are the men who grow two blades of grass in the place of one. But there cannot be much spirit of self-government about us, if we take away or allow others to take away from them almost the whole of the results of their labour. Our salvation can only come through the farmer. Neither the lawyers, nor the doctors, nor the rich landlords are going to secure it.
Now, last but not the least, it is my bounden duty to refer to what agitated our minds during these two or three days. All of us have had many anxious moments while the Viceroy was going through the streets of Benares. There were detectives stationed in many places. We were horrified. We asked ourselves, ‘Why this distrust?’ Is it not better that even Lord Hardinge should die than live a living death? But a representative of a mighty sovereign may not. He might find it necessary to impose these detectives on us? We may foam, we may fret, we may resent, but let us not forget that India of today in her impatience has produced an army of anarchists. I myself am an anarchist, but of another type. But there is a class of anarchists amongst us, and if I was able to reach this class, I would say to them that their anarchism has no room in India, if India is to conquer the conqueror. It is a sign of fear. If we trust and fear God, we shall have to fear no one, not the maharajas, not the viceroys, not the detectives, not even King George.
I myself am an anarchist, but of another type. But there is a class of anarchists amongst us, and if I was able to reach this class, I would say to them that their anarchism has no room in India, if India is to conquer the conqueror. It is a sign of fear. If we trust and fear God, we shall have to fear no one, not the maharajas, not the viceroys, not the detectives, not even King George.
I honour the anarchist for his love of the country. I honour him for his bravery in being willing to die for his country; but I ask him— is killing honourable? Is the dagger of an assassin a fit precursor of an honourable death? I deny it. There is no warrant for such methods in any scriptures. If I found it necessary for the salvation of India that the English should retire, that they should be driven out, I would not hesitate to declare that they would have to go, and I hope I would be prepared to die in defense of that belief. That would, in my opinion, be an honourable death. The bombthrower creates secret plots, is afraid to come out into the open, and when caught pays the penalty of misdirected zeal.
I have been told, ‘Had we not done this, had some people not thrown bombs, we should never have gained what we have got with reference to the partition movement.’ (Mrs Besant: ‘Please stop it.’) This was what I said in Bengal when Mr Lyon presided at the meeting. I think what I am saying is necessary. If I am told to stop I shall obey. (Turning to the Chairman) I await your orders. If you consider that by my speaking as I am, I am not serving the country and the empire I shall certainly stop. (Cries of ‘Go on.’) (The Chairman: ‘Please, explain your object.’) I am simply… (another interruption). My friends, please do not resent this interruption. If Mrs Besant this evening suggests that I should stop, she does so because she loves India so well, and she considers that I am erring in thinking audibly before you young men. But even so, I simply say this, that I want to purge India of this atmosphere of suspicion on either side, if we are to reach our goal; we should have an empire which is to be based upon mutual love and mutual trust. Is it not better that we talk under the shadow of this college than that we should be talking irresponsibly in our homes? I consider that it is much better that we talk these things openly. I have done so with excellent results before now. I know that there is nothing that the students do not know. I am, therefore, turning the searchlight towards ourselves. I hold the name of my country so dear to me that I exchange these thoughts with you, and submit to you that there is no room for anarchism in India. Let us frankly and openly say whatever we want to say our rulers, and face the consequences if what we have to say does not please them. But let us not abuse.
I was talking the other day to a member of the much-abused Civil Service. I have not very much in common with the members of that Service, but I could not help admiring the manner in which he was speaking to me. He said: ‘Mr Gandhi, do you for one moment suppose that all we, Civil Servants, are a bad lot, that we want to oppress the people whom we have come to govern?’ ‘No,’ I said. ‘Then if you get an opportunity put in a word for the much-abused Civil Service.’ And I am here to put in that word. Yes, many members of the Indian Civil Service are most decidedly overbearing; they are tyrannical, at times thoughtless. Many other adjectives may be used. I grant all these things and I grant also that after having lived in India for a certain number of years some of them become somewhat degraded. But what does that signify? They were gentlemen before they came here, and if they have lost some of the moral fibre, it is a reflection upon ourselves.
Just think out for yourselves, if a man who was good yesterday has become bad after having come in contact with me, is he responsible that he has deteriorated or am I? The atmosphere of sycophancy and falsity that surrounds them on their coming to India demoralizes them, as it would many of us. It is well to take the blame sometimes. If we are to receive self-government, we shall have to take it. We shall never be granted self-government. Look at the history of the British Empire and the British nation; freedom loving as it is, it will not be a party to give freedom to a people who will not take it themselves. Learn your lesson if you wish to from the Boer War. Those who were enemies of that empire only a few years ago have now become friends…
If we are to receive self-government, we shall have to take it. We shall never be granted self-government. Look at the history of the British Empire and the British nation; freedom loving as it is, it will not be a party to give freedom to a people who will not take it themselves. Learn your lesson if you wish to from the Boer War. Those who were enemies of that empire only a few years ago have now become friends…
(At this point there was an interruption and a movement on the platform to leave. The speech, therefore, ended here abruptly).

Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay
If you peep into the dim unknown history of India, the history of which is written not on palm leaves or papers, but is alive in the hearts of everyone of us, you will find that the position of women was indeed an enviable one. Never in the history of any country, at any time, has woman been so honoured as she has been in this country. Though apparently she seems to have lost her voice, she has always been the vital element in the evolution of the country and the nation. When I was travelling abroad, I was often asked how the suffragist movement in India was progressing. I could only tell them that there was no suffragist movement in India. In fact, there was no need for such a movement. The last few years have proved this. As soon as the new reforms came in the franchise was granted, and closely following upon its heels came the removal of the ban on sex-disqualification. The time has now come when women should come forward and share the responsibilities equally with men. All over the world women are now taking a keen and an active part in all departments of life.
The time has now come when women should come forward and share the responsibilities equally with men. All over the world women are now taking a keen and an active part in all departments of life.
I stand now as an Independent. I stand for no party or community. I stand as a representative of women. I am not a Swarajist candidate and I am not a member of the Swarajya Party. I do not believe in the policy of obstruction and walk-out. What the Swarajya programme for this year is, I do not know. Whether it is going to accept office or not, does not concern me. That temptation does not come in my way.
People have been questioning me what my political precedents are. I have been interested in politics for several years now. When the great Non-Co-operation Movement was started, my husband and I were pursuing studies in England. The great message came to us over the waters. Our hearts throbbed to the cries of the great nation. Gandhi’s message of love thrilled us, and we felt that we should not be led away by the glamor of foreign degrees. A golden opportunity had been offered to us to do our bit for our country. By the time we had completed our tour and landed in India, Mahatamaji had been imprisoned for some time. When we landed in India we were met by Mrs. [Sarojini] Naidu. The first question we asked her was: What was the condition of the country? She said there was no condition at all. Death had already set in. Our burning spirits were as defeated with this reply. We enlisted ourselves as Congress members and and tried to do our bit, but a good many difficulties arose in our way.
We soon found much of our precious time getting scattered. We then decided to do the same work through the arts and achieve the same end. So at the Belgaum Congress, we consulted Mahatmaji. He gladly assented to our plans and with his blessings we started upon our work. We have been trying to wake up the political consciousness of the country through poetry, through music and through drama. It was just a month ago that we met Mahatma Gandhi in Bombay and he said: “Though I am pressed with heavy work, I have found time to watch with pleasure your progress. Though I cannot be with you in person, let me admire you from a distance. When you have a little leisure come to my Ashram and show my boys the beauties of your art.” Even on the day I was leaving for Mangalore we received two wires asking us to go to him. It was indeed a great temptation I had to resist. All these three years, though I have not been active in the political field, all the time I have been in close touch with politics.
If women in other countries have proved competent enough to handle these problems I do not think an Indian woman will prove an exception. For years you have been sending men to the councils. Some of them have done something for this district. Others have done nothing. So even if a woman fails to fulfill your expectations you have not much to regret.
As to what work I shall do in the council, though no doubt I shall try to tackle problems that are intimately connected with women and children, I feel confident that with time and study I shall be in a position to handle general questions as well. During the course of my tour I have been observing and studying the local grievances. I have been trying to get first-hand information as to the Forest and Land Act. Some of the main problems agitating the public mind just now are the abolition of the old Rent Recovery Act without the introduction of any new compensating one and the Revenue Settlement Act. I have enough of leisure at my disposal to devote it to this work. I appeal to you to give me a chance. If women in other countries have proved competent enough to handle these problems I do not think an Indian woman will prove an exception. For years you have been sending men to the councils. Some of them have done something for this district. Others have done nothing. So even if a woman fails to fulfill your expectations you have not much to regret. Some of you may have some conscientious objections in supporting my candidature either on the ground of sex or otherwise. I appeal to them in that case, at least, to remain neutral as far as possible.
For, remember, when you work against me, you insult all womankind, you work against your own mothers, your sisters, your daughters.
When you lend me your support, it is not merely a personal favour you do to me, but you pay your homage to womankind. If the first Indian woman who has come forward in spite of all difficulties and obstacles is not helped, it will greatly discourage the women who in the future might stand for elections. So the privilege granted to women will be hardly of any service.
When you lend me your support, it is not merely a personal favour you do to me, but you pay your homage to womankind. If the first Indian woman who has come forward in spite of all difficulties and obstacles is not helped, it will greatly discourage the women who in the future might stand for elections. So the privilege granted to women will be hardly of any service. I am not concerned very much with the result. I shall do my best. I wish to prove to the world that a woman can fight and fight well in spite of everything. Woman in India has always stood for strength and not weakness. She is the Divine Shakti. Whether it is a mere sentiment or a living flame, will be proved by the elections.
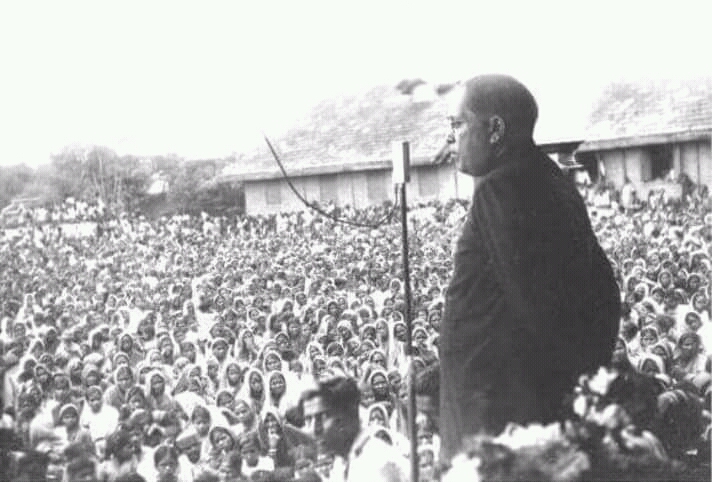

B.R. Ambedkar
Gentlemen, you have gathered here today in response to the invitation of the Satyagraha Committee. As the Chairman of that Committee, I gratefully welcome you all.
Many of you will remember that on the 19th of last March all of us came to the Chavadar Lake here. The caste Hindus of Mahad had laid no prohibition on us; but they showed they had objections to our going there by the attack they made. The fight brought results that one might have expected. The aggressive caste Hindus were sentenced to four months’ rigorous imprisonment, and are now in jail. If we had not been hindered on 19th March, it would have been proved that the caste Hindus acknowledge our right to draw water from the lake, and we should have had no need to begin our present undertaking.
Unfortunately we were thus hindered, and we have been obliged to call this meeting today. This lake at Mahad is public property. The caste Hindus of Mahad are so reasonable that they not only draw water from the lake themselves but freely permit people of any religion to draw water from it, and accordingly people of other religions such as the Islamic do make use of this permission. Nor do the caste Hindus prevent members of species considered lower than the human, such as birds and beasts, from drinking at the lake. Moreover, they freely permit beasts kept by untouchables to drink at the lake.
Caste Hindus are the very founts of compassion. They practise no hinsa and harass no one. They are not of the class of miserly and selfish folk who would grudge even a crow some grains of the food they are eating. The proliferation of sanyasis and mendicants is a living testimony to their charitable temperament. They regard altruism as religious merit and injury to another as a sin.
Even further, they have imbibed the principle that injury done by another must not be repaid but patiently endured, and so, they not only treat the harmless cow with kindness, but spare harmful creatures such as snakes. That one Atman or Spiritual Self dwells in all creatures has become a settled principle of their conduct. Such are the caste Hindus who forbid some human beings of their own religion to draw water from the Same Chavadar Lake! One cannot help asking the question, why do they forbid us alone?
Such are the caste Hindus who forbid some human beings of their own religion to draw water from the Same Chavadar Lake! One cannot help asking the question, why do they forbid us alone?
It is essential that all should understand thoroughly the answer to this question. Unless you do, I feel, you will not grasp completely the importance of today’s meeting. The Hindus are divided, according to sacred tradition, into four castes; but according to custom, into five: Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, Shudras and Atishudras. The caste system is the first of the governing rules of the Hindu religion. The second is that the castes are of unequal rank. They are ordered in a descending series of each meaner than the one before.
Not only are their ranks permanently fixed by the rule, but each is assigned boundaries it must not transgress, so that each one may at once be recognized as belonging to its particular rank. There is a general belief that the prohibitions in the Hindu religion against intermarriage, interdining, inter drinking and social intercourse are bounds set to degrees of association with one another. But this is an incomplete idea. These prohibitions are indeed limits to degrees of association; but they have been set to show people of unequal rank what the rank of each is. That is, these bounds are symbols of inequality.
Just as the crown on a man’s head shows he is a king, and the bow in his hand shows him to be a Kshatriya, the class to which none of the prohibitions applies is considered the highest of all and the one to which they all apply is reckoned the lowest in rank. The strenuous efforts made to maintain the prohibitions are for the reason that, if they are relaxed, the inequality settled by religion will break down and equality will take its place.
The caste Hindus of Mahad prevent the untouchables from drinking the water of the Chavadar Lake not because they suppose that the touch of the untouchables will pollute the water or that it will evaporate and vanish. Their reason for preventing the untouchables from drinking it is that they do not wish to acknowledge by such a permission that castes declared inferior by sacred tradition are in fact their equals.
Gentlemen! you will understand from this the significance of the struggle we have begun. Do not let yourselves suppose that the Satyagraha Committee has invited you to Mahad merely to drink the water of the Chavadar Lake of Mahad.
It is not as if drinking the water of the Chavadar Lake will make us immortal. We have survived well enough all these days without drinking it. We are not going to the Chavadar Lake merely to drink its water. We are going to the Lake to assert that we too are human beings like others. It must be clear that this meeting has been called to set up the norm of equality.
It is not as if drinking the water of the Chavadar Lake will make us immortal. We have survived well enough all these days without drinking it. We are not going to the Chavadar Lake merely to drink its water. We are going to the Lake to assert that we too are human beings like others. It must be clear that this meeting has been called to set up the norm of equality.
I am certain that no one who thinks of this meeting in this light will doubt that it is unprecedented. I feel that no parallel to it can be found in the history of India. If we seek for another meeting in the past to equal this, we shall have to go to the history of France on the continent of Europe. A hundred and thirty-eight years ago, on 24 January 1789, King Louis XVI had convened, by royal command, an assembly of deputies to represent the people of the kingdom. His French National Assembly has been much vilified by historians. The Assembly sent the King and the Queen of France to the guillotine; persecuted and massacred the aristocrats; and drove their survivors into exile. It confiscated the estates of the rich and plunged Europe into war for fifteen years. Such are the accusations leveled against the Assembly by the historians. In my view, the criticism is misplaced; further, the historians of this school have not understood the gist of the achievement of the French National Assembly. That achievement served the welfare not only of France but of the entire European continent. If European nations enjoy peace and prosperity today, it is for one reason: the revolutionary French National Assembly convened in 1789 set new principles for the organization of society before the disorganized and decadent French nation of its time, and the same principles have been accepted and followed by Europe.
To appreciate the importance of the French National Assembly and the greatness of its principles, we must keep in mind the suite of French society at the time. You are all aware that our Hindu society is based on the system of castes. A rather similar system of classes existed in the France of 1789: the difference was that it was a society of three castes. Like the Hindu society, the French had a class of Brahmins and another of Kshatriyas. But instead of three different castes of Vaishya, Shudra, and Atishudra, there was one class that comprehended these. This is a minor difference. The important thing is that the caste or class system was similar. The similarity to be noted is not only in the differentiation between classes: the inequality of our caste system was also to be found in the French social system. The nature of the inequality in the French society was different: it was economic in nature. It was, however, equally intense. The thing to bear in mind is there is a great similarity between the French National Assembly that met on 5 May 1789 at Versailles and our meeting today. The similarity is not only in the circumstances in which the two meetings took place but also in their ideals.
That Assembly of the French people was convened to reorganize French society. Our meeting today too has been convened to reorganize Hindu society. Hence, before discussing on what principles our society should be reorganized, we should all pay heed to the principles on which the French Assembly relied and the policy it adopted. The scope of the French Assembly was far wider than that of our present meeting. It had to carry out the threefold organization of the French political, social and religious systems. We must confine ourselves to how social and religious reorganization can be brought about. Since we are not, for the present, concerned with political reorganization, let us see what the French Assembly did in the matter of the religious and social reorganization of their nation. The policy adopted by the French National Assembly in this area can be seen plainly by anyone from three important proclamations issued by that Assembly. The first was issued on 17 June 1789. This was a proclamation about the class systems in France. As said before, French society was divided into three classes. The proclamation abolished the three classes and blended them into one. Further, it abolished the seats reserved separately for the three classes (or estates) in the political assembly. The second proclamation was about the priests. By ancient custom, to appoint or remove these priests was outside the power of the nation, that being the monopoly of a foreign religious potentate, the Pope. Anyone appointed by the Pope was a priest, whether or not he was fit to be one in the eyes of those to whom he was to preach. The proclamation abolished the autonomy of the religious orders and assigned to the French nation the authority to decide who might follow this vocation, who was fit for it and who was not, whether he was to be paid for preaching or not, and so on. The third proclamation was not about the political, economic or religious systems. It was of a general nature and laid down the principles on which all social arrangements ought to rest. From that point of view, the third proclamation is the most important of the three; it might be called the king of these proclamations. It is renowned the world over as the declaration of human birthrights. It is not only unprecedented in the history of France; more than that, it is unique in the history of civilized nations. For every European nation has followed the French Assembly in giving it a place in its own constitution. So one may say that it brought about a revolution not only in France but the whole world. This proclamation has seventeen clauses, of which the following are important:
Any person is free to act according to his birthright. Any limit placed upon this freedom must be only to the extent necessary to permit other persons to enjoy their birthrights. Such limits must be laid down by law: they cannot be set on the grounds of the religion or on any other basis than the law of the land.
1) All human beings are equal by birth; and they shall remain equal till death. They may be distinguished in status only in the public interest. Otherwise, their equal status must be maintained.
2) The ultimate object of politics is to maintain these human birthrights.
3) The entire nation is the mother-source of sovereignty. The rights of any individual, group or special class, unless they are given by the nation, cannot be acknowledged as valid on any other ground, be it political or religious.
4) Any person is free to act according to his birthright. Any limit placed upon this freedom must be only to the extent necessary to permit other persons to enjoy their birthrights. Such limits must be laid down by law: they cannot be set on the grounds of the religion or on any other basis than the law of the land.
5) The law will forbid only such actions as are injurious to society. All must be free to do what has not been forbidden by law. Nor can anyone be compelled to do what the law has not laid down as a duty.
6) The law is not in the nature of bounds set by any particular class. The right to decide what the law shall be rests with the people or their representatives. Whether such a law is protective or punitive, it must be the same for all. Since justice requires that all social arrangements be based on the equality of all, all individuals are equally eligible for any kind of honour, power and profession. Any distinction in such matters must be owing to differences of individual merit; it must not be based on birth.
I feel our meeting today should keep the image of this French National Assembly before the mind. The road it marked out for the development of the French nation, the road that all progressed nations have followed, ought to be the road adopted for the development of Hindu society by this meeting. We need to pull away the nails which hold the framework of caste-bound Hindu society together, such as those of the prohibition of intermarriage down to the prohibition of social intercourse so that Hindu society becomes all of one caste. Otherwise untouchability cannot be removed nor can equality be established.
To raise men, aspiration is needed as much as outward efforts. Indeed it is to be doubted whether efforts are possible without aspiration. Hence, if a great effort is to be made, a great aspiration must be nursed. In adopting an aspiration one need not be abashed or deterred by doubts about one’s power to satisfy it. One should be ashamed only of mean aspirations; not of failure that may result because one’s aspiration is high. If untouchability alone is removed, we may change from Atishudras to Shurdas; but can we say that this radically removes untouchability? If such puny reforms as the removal of restrictions on social intercourse etc. were enough for the eradication of untouchability I would not have suggested that the caste system itself must go.
Some of you may feel that since we are untouchables, it is enough if we are set free from the prohibitions of interdrinking and social intercourse. That we need not concern ourselves with the caste system; how does it matter if it remains? In my opinion, this is a total error. If we leave the caste system alone and adopt only the removal of untouchability as our policy, people will say that we have chosen a low aim. To raise men, aspiration is needed as much as outward efforts. Indeed it is to be doubted whether efforts are possible without aspiration. Hence, if a great effort is to be made, a great aspiration must be nursed. In adopting an aspiration one need not be abashed or deterred by doubts about one’s power to satisfy it. One should be ashamed only of mean aspirations; not of failure that may result because one’s aspiration is high. If untouchability alone is removed, we may change from Atishudras to Shurdas; but can we say that this radically removes untouchability? If such puny reforms as the removal of restrictions on social intercourse etc. were enough for the eradication of untouchability I would not have suggested that the caste system itself must go. Gentlemen! You all know that if a snake is to be killed it is not enough to strike at its tail – its head must be crushed. If any harm is to be removed, one must seek out its root and strike at it. An attack must be based on the knowledge of the enemy’s vital weakness. Duryodhana was killed because Bheema struck at his thigh with his mace. If the mace had hit Durydhana’s head he would not have died; for his thigh was his vulnerable spot. One finds many instances of a physician’s efforts to remove a malady proving fruitless because he has not perceived fully what will get rid of the disease; similar instances of failure to root out a social disease when it is not fully diagnosed are rarely recorded in history; and so one does not often become aware of them. But let me acquaint you with one such instance that I have come across in my reading. In the ancient European nation of Rome, the patricians were considered upper class, and the plebians, lower class. All power was in the hands of, the patricians, and they used it to ill-treat the plebians. To free themselves from this harassment, the plebians, on the strength of their unity, insisted that laws should be written down for the facilitation of justice and for the information of all. Their patrician opponents agreed to this; and a charter of twelve laws was written down. But this did not rid the oppressed plebians of their woes. For the officers who enforced the laws were all of the patrician class; moreover, the chief officer, called the tribune, was also a patrician. Hence, though the laws were uniform, there was partiality in their enforcement. The plebians then demanded that instead of the administration being in the hands of one tribune there should be two tribunes, of whom one should be elected by the plebians and the other by the patricians. The patricians yielded to this too, and the plebians rejoiced, supposing they would now be free of their miseries. But their rejoicing was short-lived. The Roman people had a tradition that nothing was to be done without the favourable verdict of the oracle at Delphi. Accordingly, even the election of a duly elected tribune – if the oracle did not approve of him – had to be treated as annulled, and another had to be elected, of whom the oracle approved. The priest who put the question to the oracle was required, by sacred religious custom, to be one born of parents married in the mode the Romans called conferatio and this mode of marriage prevailed only among the patricians; so that the priest of Delphi was always a patrician.
The wily priest always saw to it that if the plebians elected a man really devoted to their cause, the oracle went against him. Only if the man elected by the plebians to the position of tribune was amenable to the patricians, would the oracle favour him and give him the opportunity of actually assuming office. What did the plebians gain by their right to elect a tribune? The answer must be, nothing in reality. Their efforts proved meaningless because they did not trace the malady to its source. If they had, they would, at the same time that they demanded a tribune of their election, have also settled the question of who should be the priest at Delphi. The disease could not be eradicated by demanding a tribune; it needed control of the priestly office; which the plebians failed to perceive. We too, while we seek a way to remove untouchability, must inquire closely into what will eradicate the disease; otherwise we too may miss our aim. Do not be foolish enough to believe that removal of the restrictions on social intercourse or interdrinking will remove untouchability.
Remember that if the prohibitions on social intercourse and interdrinking go, the roots of untouchability are not removed. Release from these two restrictions will, at the most, remove untouchability as it appears outside the home; but it will leave untouchability in the home untouched. If we want to remove untouchability in the home as well as outside, we must break down the prohibition against intermarriage. Nothing else will serve. From another point of view, we see that breaking down the bar against intermarriage is the way to establish real equality. Anyone must confess that when the root division is dissolved, incidental points of separateness will disappear by themselves. The interdictions on interdining, interdrinking and social intercourse have all sprung from the one interdiction against intermarriage. Remove the last and no special efforts are needed to move the rest. They will disappear of their own accord. In my view the removal of untouchability consists in breaking down the ban on intermarriage and doing so will establish real equality. If we wish to cut out untouchability, we must recognize that the root of untouchability is in the ban on intermarriage. Even if our attack today is on the ban against interdrinking, we must press it home against the ban on intermarriage; otherwise untouchability cannot be removed by the roots. Who can accomplish this task? It is no secret that the Brahmin class cannot do it.
If we wish to cut out untouchability, we must recognize that the root of untouchability is in the ban on intermarriage. Even if our attack today is on the ban against interdrinking, we must press it home against the ban on intermarriage; otherwise untouchability cannot be removed by the roots. Who can accomplish this task? It is no secret that the Brahmin class cannot do it.
While the caste system lasts, the Brahmin caste has its supremacy. No one, of his own will, surrenders power which is in his hands. The Brahmins have exercised their sovereignty over all other castes for centuries. It is not likely that they will be willing to give it up and treat the rest as equals. The Brahmins do not have the patriotism of the Samurais of Japan. It is useless to hope that they will sacrifice their privileges as the Samurai class did, for the sake of national unity based on a new equality. Nor does it appear likely that the task will be carried out by other caste Hindus. These others, such as the class comprising the Marathas and other similar castes, are a class between the privileged and those without any rights.
A privileged class, at the cost of a little self-sacrifice, can show some generosity. A class without any privileges has ideals and aspirations; for, at least as a matter of self-interest, it wishes to bring about a social reform. As a result it develops an attachment to principles rather than to self-interest. The class of caste Hindus, other than Brahmins, lies in between: it cannot practise the generosity possible to the class above and it does not develop the attachment to principles that develops in the class below. This is why this class is seen to be concerned not so much about attaining equality with the Brahmins as about maintaining its status above the untouchables.
For the purposes of the social reform required, the class of caste Hindus other than Brahmins is feeble. If we are to await its help, we should fall into the difficulties that the farmer faced, who depended on his neighbour’s help for his harvesting, as in the story of the mother lark and her chicks found in many textbooks.
The task of removing untouchability and establishing equality that we have undertaken, we must carry out ourselves. Others will not do it. Our life will gain its true meaning if we consider that we are born to carry out this task and set to work in earnest. Let us receive this merit which is awaiting us.
The task of removing untouchability and establishing equality that we have undertaken, we must carry out ourselves. Others will not do it. Our life will gain its true meaning if we consider that we are born to carry out this task and set to work in earnest. Let us receive this merit which is awaiting us.
This is a struggle in order to raise ourselves; hence we are bound to undertake it, so as to remove the obstacles to our progress. We all know how at every turn, untouchability muddies and soils our whole existence. We know that at one time our people were recruited in large numbers into the troops. It was a kind of occupation socially assigned to us and few of us needed to be anxious about earning our bread. Other classes of our level have found their way into the troops, the police, the courts and the offices, to earn their bread. But in the same areas of employment you will no longer find the untouchables.
It is not that the law debars us from these jobs. Everything is permissible as far the law is concerned. But the Government finds itself powerless because other Hindus consider us untouchables and look down upon us, and it acquiesces in our being kept out of Government jobs. Nor can we take up any decent trade. It is true, partly, that we lack money to start business, but the real difficulty is that people regard us as untouchables and no one will accept goods from our hands.
To sum up, untouchability is not a simple matter; it is the mother of all our poverty and lowliness and it has brought us to the abject state we are in today. If we want to raise ourselves out of it, we must undertake this task. We cannot be saved in any other way. It is a task not for our benefit alone; it is also for the benefit of the nation.
Untouchability is not a simple matter; it is the mother of all our poverty and lowliness and it has brought us to the abject state we are in today. If we want to raise ourselves out of it, we must undertake this task. We cannot be saved in any other way. It is a task not for our benefit alone; it is also for the benefit of the nation.
Hindu society must sink unless the untouchability that has become a part of the four-castes system is eradicated. Among the resources that any society needs in the struggle for life, a great resource is the moral order of that society. And everyone must admit that a society in which the existing moral order upholds things that disrupt the society and condemns those that would unite the members of the society, must find itself defeated in any struggle for life with other societies. A society which has the opposite moral order, one in which things that unite are considered laudable and things that divide are condemned, is sure to succeed in any such struggle.
This principle must be applied to Hindu society. Is it any wonder that it meets defeat at every turn when it upholds a social order that fragments its members, though it is plain to anyone who sees it that the four-castes system is such a divisive force and that a single caste for all, would unite society? If we wish to escape these disastrous conditions, we must break down the framework of the four-castes system and replace it by a single caste system.
Even this will not be enough. The inequality inherent in the four-castes system must be rooted out. Many people mock at the principles of equality. Naturally, no man is another’s equal. One has an impressive physique; another is slow-witted. The mockers think that, in view of these inequalities that men are born with, the egalitarians are absurd in telling us to regard them as equals. One is forced to say that these mockers have not understood fully the principle of equality.
If the principle of equality means that privilege should depend, not on birth, wealth, or anything else, but solely on the merits of each man, then how can it be demanded that a man without merit, and who is dirty and vicious, should be treated on a level with a man who has merit and is clean and virtuous? Such is a counter-question sometimes posed. It is essential to define equality as giving equal privileges to men of equal merit.
But before people have had an opportunity to develop their inherent qualities and to merit privileges, it is just to treat them all equally. In sociology, the social order is itself the most important factor in the full development of qualities that any person may possess at birth. If slaves are constantly treated unequally, they will develop no qualities other than those appropriate to slaves, and they will never become fit for any higher status. If the clean man always repulses the unclean man and refuses to have anything to do with him, the unclean man will never develop the aspiration to become clean. If the criminal or immoral castes are given no refuge by the virtuous castes, the criminal castes will never learn virtue.
The examples given above show that, although an equal treatment may not create good qualities in one who does not have them at all, even such qualities where they exist need equal treatment for their development; also, developed good qualities are wasted and frustrated without equal treatment.
On the one hand, the inequality in Hindu society stuns the progress of individuals and in consequence stunts society. On the other hand, the same inequality prevents society from bringing into use powers stored in individuals. In both ways, this inequality is weakening Hindu society, which is in disarray because of the four-castes system.
Hence, if Hindu society is to be strengthened, we must uproot the four-castes system and untouchability, and set the society on the foundations of the two principles of one caste only and of equality. The way to abolish untouchability is not any other than the way to invigorate Hindu society. Therefore I say that our work is beyond doubt as much for the benefit of the nation as it is in our own interest.
If Hindu society is to be strengthened, we must uproot the four-castes system and untouchability, and set the society on the foundations of the two principles of one caste only and of equality. The way to abolish untouchability is not any other than the way to invigorate Hindu society. Therefore I say that our work is beyond doubt as much for the benefit of the nation as it is in our own interest.
Our work has been begun to bring about a real social revolution. Let no one deceive himself by supposing that it is a diversion to quieten minds entranced with sweet words. The work is sustained by strong feeling, which is the power that drives the movement. No one can now arrest it. I pray to God that the social revolution which begins here today may fulfill itself by peaceful means.
None can doubt that the responsibility of letting the revolution take place peacefully rests more heavily on our opponents than on us. Whether this social revolution will work peacefully or violently will depend wholly on the conduct of the caste Hindus. People who blame the French National Assembly of 1789 for atrocities forget one point. That is, if the rulers of France had not been treacherous to the Assembly, if the upper classes had not resisted it, had not committed the crime of trying to suppress it with foreign help, it would have had no need to use violence in the work of the revolution and the whole social transformation would have been accomplished peacefully.
We say to our opponents too: please do not oppose us. Put away the orthodox scriptures. Follow justice. And we assure you that we shall carry out our programme peacefully.
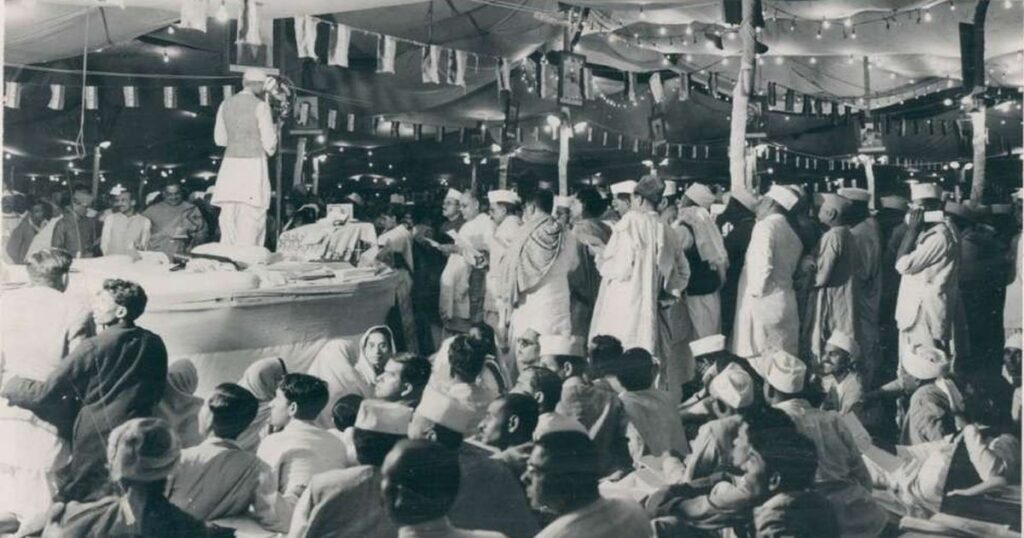

Pledge for Purna Swaraj, Jawaharlal Nehru
Comrades— for four and forty years this National Congress has laboured for the freedom of India. During this period it has somewhat slowly, but surely, awakened national consciousness from its long stupor and built up the national movement. If, today we are gathered here at a crisis of our destiny, conscious of our strength as well as of our weakness, and looking with hope and apprehension to the future, it is well that we give first thought to those who have gone before us and who spent out their lives with little hope of reward, so that those that followed them may have the joy of achievement. Many of the giants of old are not with us and we of a later day, standing on an eminence of their creation, may often decry their efforts. That is the way of the world. But none of you can forget them or the great work they did in laying the foundations of a free India. And none of us can ever forget that glorious band of men and women who, without tacking the consequences, have laid down their young lives or spent their bright youth in suffering and torment in utter protest against a foreign domination.
Many of their names even are not known to us. They laboured and suffered in silence without any expectation of public applause, and by their heart’s blood they nursed the tender plant of India’s freedom. While many of us temporized and compromised, they stood up and proclaimed a people’s right to freedom and declared to the world that India, even in her degradation, had the spark of life in her, because she refused to submit to tyranny and serfdom. Brick by brick has our national movement been built up, and often on the prostrate bodies of her martyred sons has India advanced. The giants of old may not be with us, but the courage of old is with us still and India can yet produce martyrs like Jatin Das and Wizaya. This is the glorious heritage that we have inherited and you wish to put me in charge of it. I know well that I occupy this honoured place by chance more than by your deliberate design. Your desire was to choose another — one who towers above all others in this present day world of ours — and there could have been no wiser choice. But fate and he conspired together and thrust me against your will and mine into this terrible seat of responsibility. Should I express my gratitude to you for having placed me in this dilemma? But I am grateful indeed for your confidence in one who strangely lacks it himself.
Brick by brick has our national movement been built up, and often on the prostrate bodies of her martyred sons has India advanced. The giants of old may not be with us, but the courage of old is with us still and India can yet produce martyrs like Jatin Das and Wizaya. This is the glorious heritage that we have inherited and you wish to put me in charge of it.
You will discuss many vital national problems that face us today and your decisions may change the course of Indian history. But you are not the only people that are faced with problems. The whole world today is one vast question-mark and every country and every people is in the melting pot. The age of faith, with the comfort and stability it brings, is past and there is questioning about everything, however permanent or sacred it might have appeared to our forefathers. Everywhere, there is doubt and restlessness and the foundations of the state and society are in process of transformation. Old established ideas of liberty, justice, property, and even the family are being attacked and the outcome hangs in the balance. We appear to be in a dissolving period of history when the world is in labour and out of her travail will give birth to a new order.
The future lies with America and Asia. Owing to false and incomplete history many of us have been led to think that Europe has always dominated over the rest of the world, and Asia has always let the legions of the West thunder past and plunged in thought again. We have forgotten that for millennia the legions of Asia overran Europe and modern Europe itself largely consists of the descendants of these invaders from Asia. We have forgotten that it was India that finally broke the military power of Alexander.
No one can say what the future will bring, but we may assert with some confidence that Asia and even India, will play a determining part in future world policy. The brief day of European domination is already approaching its end. Europe has ceased to be the centre of activity and interest. The future lies with America and Asia. Owing to false and incomplete history many of us have been led to think that Europe has always dominated over the rest of the world, and Asia has always let the legions of the West thunder past and plunged in thought again. We have forgotten that for millennia the legions of Asia overran Europe and modern Europe itself largely consists of the descendants of these invaders from Asia. We have forgotten that it was India that finally broke the military power of Alexander.
Thought has undoubtedly been the glory of Asia and specially of India, but in the field of action the record of Asia has been equally great. But none of us desires that the legions of Asia or Europe should overrun the continents again. We have all had enough of them.
India today is a part of a world movement. Not only China, Turkey, Persia, and Egypt but also Russia and the countries of the West are taking part in this movement, and India cannot isolate herself from it. We have our own problems — difficult and intricate — and we cannot run away from them and take shelter in the wider problems that affect the world. But if we ignore the world, we do so at our peril. Civilization today, such as it is, is not the creation or monopoly of one people or nation. It is a composite fabric to which all countries have contributed and then have adapted to suit their particular needs. And if India has a message to give to the world as I hope she has, she has also to receive and learn much from the messages of other peoples.
Few things in history are more amazing than the wonderful stability of the social structure in India, which withstood the impact of numerous alien influences and thousands of years of change and conflict. It withstood them because it always sought to absorb them and tolerate them. Its aim was not to exterminate, but to establish an equilibrium between different cultures. Aryans and non-Aryans settled down together recognizing each other’s right to their culture, and outsiders who came, like the Parsis, found a welcome and a place in the social order. With the coming of the Muslims, the equilibrium was disturbed, but India sought to restore it, and largely succeeded. Unhappily for us before we could adjust our differences, the political structure broke down, the British came and we fell.
When everything is changing it is well to remember the long course of Indian history. Few things in history are more amazing than the wonderful stability of the social structure in India, which withstood the impact of numerous alien influences and thousands of years of change and conflict. It withstood them because it always sought to absorb them and tolerate them. Its aim was not to exterminate, but to establish an equilibrium between different cultures. Aryans and non-Aryans settled down together recognizing each other’s right to their culture, and outsiders who came, like the Parsis, found a welcome and a place in the social order. With the coming of the Muslims, the equilibrium was disturbed, but India sought to restore it, and largely succeeded. Unhappily for us before we could adjust our differences, the political structure broke down, the British came and we fell.
Great as was the success of India in evolving a stable society, she failed and in a vital particular, and because she failed in this, she fell and remains fallen. No solution was found for the problem of equality. India deliberately ignored this and built up her social structure on inequality, and we have the tragic consequences of this policy in the millions of our people who till yesterday were suppressed and had little opportunity for growth.
And yet when Europe fought her wars of religion and Christians massacred each other in the name of their saviour, India was tolerant, although alas, there is little of this toleration today. Having attained some measure of religious liberty, Europe sought after political liberty, and political and legal equality. Having attained these also, she finds that they mean very little without economic liberty and equality. And so today politics have ceased to have much meaning and the most vital question is that of social and economic equality.
India also will have to find a solution to this problem and until she does so, her political and social structure cannot have stability. That solution need not necessarily follow the example of any other country. It must, if it has to endure, be based on the genius of her people and be an outcome of her thought and culture. And when it is found, the unhappy differences between various communities, which trouble us today and keep back our freedom, will automatically disappear.
What shall we gain for ourselves or for our community, if all of us are slaves in a slave country? And what can we lose if once we remove the shackles from India and can breathe the air of freedom again? Do we want outsiders who are not of us and who have kept us in bondage, to be the protectors of our little rights and privileges, when they deny us the very right to freedom? No majority can crush a determined minority and no minority can be protected by a little addition to its seats in a legislature. Let us remember that in the world today, almost everywhere a very small minority holds wealth and power and dominates over the great majority.
Indeed, the real differences have already largely gone, but fear of each other and distrust and suspicion remain and sow seeds of discord. The problem is how to remove fear and suspicion and, being intangible, they are hard to get at. An earnest attempt was made to do so last year by the All Parties’ Committee and much progress was made towards the goal. But we must admit with sorrow that success has not wholly crowned its efforts. Many of our Muslim and Sikh friends have strenuously opposed the solutions suggested and passions have been roused over mathematical figures and percentages. Logic and cold reasons are poor weapons to fight fear and distrust. Only faith and generosity can overcome them. I can only hope that the leaders of various communities will have this faith and generosity in ample measure. What shall we gain for ourselves or for our community, if all of us are slaves in a slave country? And what can we lose if once we remove the shackles from India and can breathe the air of freedom again? Do we want outsiders who are not of us and who have kept us in bondage, to be the protectors of our little rights and privileges, when they deny us the very right to freedom? No majority can crush a determined minority and no minority can be protected by a little addition to its seats in a legislature. Let us remember that in the world today, almost everywhere a very small minority holds wealth and power and dominates over the great majority.
I have no love for bigotry and dogmatism in religion and I am glad that they are weakening. Nor do I love communalism in any shape or form. I find it difficult to appreciate why political or economic rights should depend on the membership of a religious group or community. I can fully understand the right to freedom in a religion and the right to one’s culture, and in India specially, which has always acknowledged and granted these rights, it should be no difficult matter to ensure their continuance We have only to find out some way whereby we may root out the fear and distrust that darken our horizon today. The politics of a subject race are largely based on fear and hatred, and we have been too long under subjection to get rid of them easily.
The politics of a subject race are largely based on fear and hatred, and we have been too long under subjection to get rid of them easily.
I was born a Hindu but I do not know how far I am justified in calling myself one or in speaking on behalf of Hindus. But birth still counts in this country and by right of birth I shall venture to submit to the leaders of the Hindus that it should be their privilege to take the lead in generosity. Generosity is not only good morals, but is often good politics and sound expediency. And it is inconceivable to me that in a free India, the Hindus can ever be powerless. So far as I am concerned, I would gladly ask our Muslim and Sikh friends to take what they will without protest and argument from me. I know that the time is coming soon when these labels and appellations will have little meaning and when our struggle will be on an economic basis. Meanwhile, it matters little what our mutual arrangements are, provided only that we do not build up barriers which will come in the way of our future progress.
The time has indeed already come when the All Parties’ Report has to be put aside and we march forward unfettered to our goal. You will remember that the resolution of the last Congress fixed a year of grace for the adoption of the All-Parties scheme. That year is nearly over and the natural issue of that decision is for this Congress to declare in favour of independence and devise sanctions to achieve it.
Recently, there has been a seeming offer of peace. The Viceroy has stated on behalf of the British Government that the leaders of Indian opinion will be invited to confer with the government on the subject of India’s future Constitution. The Viceroy meant well and his language was the language of peace. But even a Viceroy’s goodwill and courteous phrases are poor substitutes for the hard facts that confront us. We have sufficient experience of the devious ways of British diplomacy to beware of it. The offer which the British Government made was vague and there was no commitment or promise of performance. Only by the greatest stretch of imagination could it be interpreted as a possible response to the Calcutta resolution. Many leaders of various political parties met together soon after and considered it. They gave it the most favourable interpretation, for they desired peace and were willing to go half-way to meet it. But in courteous language they made it clear what the vital conditions for its acceptance were.
Many of us who believed in independence and were convinced that the offer was only a device to lead us astray and create division in our ranks, suffered bitter anguish and were torn with doubt. Were we justified in precipitating a terrible national struggle with all its inevitable consequences of suffering for many, when there was even an outside chance of honourable peace? With much searching of heart we signed that manifesto and I know not today if we did right or wrong. Later came the explanations and amplifications in the British Parliament and elsewhere and all doubt, if doubt there was, was removed as to the true significance of the offer. Even so your Working Committee chose to keep open the door of negotiation and left it to this Congress to take the final decision.
During the last few days there has been another discussion of this subject in the British House of Commons and the Secretary of State for India has endeavoured to point out that successive governments have tried to prove, not only by words but by deeds also, the sincerity of their faith in regard to India. We must recognize Mr Wedgwood Benn’s desire to do something for India and his anxiety to secure the goodwill of the Indian people. But his speech and other speeches made in Parliament carry us no further. ‘Dominion Status in action’, to which he has drawn attention has been a snare for us and has certainly not reduced the exploitation of India.
The burdens on the Indian masses are even greater today, because of this ‘Dominion Status in action’ and the so-called constitutional reforms of ten years ago. High Commissioners in London and representatives of the League of Nations, and the purchase of stores, and Indian Governors and high officials are no parts of our demand. We want to put an end to the exploitation of India’s poor and to get the reality of power and not merely the livery of office. Mr Wedgwood Benn has given us a record of the achievements of the past decade. He could have added to it by referring to Martial Law in the Punjab and the Jallianwala Bagh shooting and the repression and exploitation that have gone on continually during this period of ‘Dominion Status in action.’ He has given us some insight into what more of Dominion Status may mean for us. It will mean the shadow of authority to a handful of Indians and more repression and exploitation of the masses.
What will this Congress do? The conditions for cooperation remain unfulfilled. Can we cooperate so long as there is no guarantee that real freedom will come to us? Can we cooperate when our comrades lie in prison and repression continues? Can we cooperate until we are assured that real peace is sought after and not merely a tactical advantage over us? Peace cannot come at the point of the bayonet, and if we are to continue to be dominated over by an alien people, let us at least be no consenting parties to it.
What will this Congress do? The conditions for cooperation remain unfulfilled. Can we cooperate so long as there is no guarantee that real freedom will come to us? Can we cooperate when our comrades lie in prison and repression continues? Can we cooperate until we are assured that real peace is sought after and not merely a tactical advantage over us? Peace cannot come at the point of the bayonet, and if we are to continue to be dominated over by an alien people, let us at least be no consenting parties to it.
If the Calcutta resolution holds, we have but one goal today, that of independence. Independence is not a happy word in the world today; for it means exclusiveness and isolation. Civilization has had enough of narrow nationalism and gropes towards a wider cooperation and inter-dependence. And if we use the word ‘independence’, we do so in no sense hostile to the larger ideal. Independence for us means complete freedom from British domination and British imperialism. Having attained our freedom, I have no doubt that India will welcome all attempts at world-cooperation and federation, and will even agree to give up part of her own independence to a larger group of which she is an equal member.
Independence is not a happy word in the world today; for it means exclusiveness and isolation. Civilization has had enough of narrow nationalism and gropes towards a wider cooperation and inter-dependence. And if we use the word ‘independence’, we do so in no sense hostile to the larger ideal. Independence for us means complete freedom from British domination and British imperialism. Having attained our freedom, I have no doubt that India will welcome all attempts at world-cooperation and federation, and will even agree to give up part of her own independence to a larger group of which she is an equal member.
The British Empire today is not such a group and cannot be so long as it dominates over millions of people and holds large areas of the world’s surface despite the will of their inhabitants. It cannot be a true commonwealth so long as imperialism is its basis and the exploitation of other races its chief means of sustenance. The British Empire today is indeed gradually undergoing a process of political dissolution. It is in a state of unstable equilibrium. The Union of South Africa is not a happy member of the family, nor is the Irish Free State, a willing one. Egypt drifts away. India could never be an equal member of the Commonwealth unless imperialism and all it implies is discarded. So long as this is not done, India’s position in the empire must be one of subservience and her exploitation will continue.
There is talk of world-peace and pacts have been signed by the nations of the world. But despite pacts, armaments grow and beautiful language is the only homage that is paid to the goddess of peace. Peace can only come when the causes of war are removed. So long as there is the domination of one country over another, or the exploitation of one class by another, there will always be attempts to subvert the existing order and no stable equilibrium can endure. Out of imperialism and capitalism peace can never come. And it is because the British Empire stands for these and bases itself on the exploitation of the masses that we can find no willing place in it. No gain that may come to us is worth anything unless it helps in removing the grievous burdens on our masses. The weight of a great empire is heavy to carry and long our people have endured it. Their backs are bent down and their spirit has almost broken. How will they share in the Commonwealth partnership if the burden of exploitation continues? Many of the problems we have to face are the problems of vested interests mostly created or encouraged by the British Government. The interests of the Rulers of Indian States, of British officials and British capital and Indian capital and of the owners of big zamindaris are ever thrust before us, and they clamour for protection. The unhappy millions who really need protection are almost voiceless and have few advocates.
We have had much controversy about independence and Dominion Status and we have quarrelled about words. But the real thing is the conquest of power by whatever name it may be called. I do not think that any form of Dominion Status applicable to India will give us real power. A test of this power would be the entire withdrawal of the alien army of occupation and economic control. Let us, therefore, concentrate on these and the rest will follow easily.
We stand therefore today, for the fullest freedom of India. This Congress has not acknowledged and will not acknowledge the right of the British Parliament to dictate to us in any way. To it we make no appeal. But we do appeal to the Parliament and the conscience of the world, and to them we shall declare, I hope, that India submits no longer to any foreign domination. Today or tomorrow, we may not be strong enough to assert our will. We are very conscious of our weakness, and there is no boasting in us or pride of strength. But let no one, least of all England, mistake or underrate the meaning or strength of our resolve. Solemnly, with full knowledge of consequences, I hope, we shall take it and there will be no turning back. A great nation cannot be thwarted for long when once its mind is clear and resolved. If today we fail and tomorrow brings no success, the day after will follow and bring achievement.
We stand therefore today, for the fullest freedom of India. This Congress has not acknowledged and will not acknowledge the right of the British Parliament to dictate to us in any way. To it we make no appeal. But we do appeal to the Parliament and the conscience of the world, and to them we shall declare, I hope, that India submits no longer to any foreign domination. Today or tomorrow, we may not be strong enough to assert our will. We are very conscious of our weakness, and there is no boasting in us or pride of strength. But let no one, least of all England, mistake or underrate the meaning or strength of our resolve. Solemnly, with full knowledge of consequences, I hope, we shall take it and there will be no turning back. A great nation cannot be thwarted for long when once its mind is clear and resolved. If today we fail and tomorrow brings no success, the day after will follow and bring achievement.
We are weary of strife and hunger for peace and opportunity to work constructively for our country. Do we enjoy the breaking up of our homes and the sight of our brave young men going to prison or facing the halter? Does the worker like going on strike to lose even his miserable pittance and starve? He does so by sheer compulsion when there is no other way for him. And we who take this perilous path of national strife do so because there is no other way to an honourable peace. But we long for peace, and the hand of fellowship will always be stretched out to all who may care to grasp it. But behind the hand will be a body which will not bend to injustice and a mind that will not surrender on any vital point.
With the struggle before us, the time for determining our future Constitution is not yet. For two years or more we have drawn up constitutions and finally the All-Parties’ Committee put a crown to these efforts by drawing up a scheme of its own which the Congress adopted for a year. The labour that went to the making of this scheme was not wasted and India has profited by it. But the year is past and we have to face new circumstances which require action rather than constitution-making. Yet we cannot ignore the problems that beset us and that will make or mar our struggle and our future constitution. We have to aim at social adjustment and equilibrium and to overcome the forces of disruption that have been the bane of India.
I must frankly confess that I am a socialist and a republican and am no believer in kings and princes, or in the order which produces the modern kings of industry, who have greater power over the lives and fortunes of men than even kings of old, and whose methods are as predatory as those of the old feudal aristocracy. I recognize, however, that it may not be possible for a body constituted as in this National Congress and in the present circumstances of the country to adopt a full socialistic programme. But we must realize that the philosophy of socialism has gradually permeated the entire structure of society the world over and almost the only points in dispute are the pace and methods of advance to its full realization. India will have to go that way too if she seeks to end her poverty and inequality, though she may evolve her own methods and may adapt the ideal to the genuine of her race.
We have three major problems, the minorities, the Indian states, and labour and peasantry. I have dealt already with the question of minorities. I shall only repeat that we must give the fullest assurance by our words and our deeds that their culture and traditions will be safe.
The Indian states cannot live apart from the rest of India and their rulers must, unless they accept their inevitable limitations, go the way of others who thought like them. And the only people who have a right to determine the future of the states must be the people of these states, including the rulers. This Congress which claims self-determination cannot deny it to the people of the states. Meanwhile, the Congress is perfectly willing to confer with such rulers as are prepared to do so and to devise means whereby the transition may not be too sudden. But in no event can the people of the states be ignored.
Our third major problem is the biggest of all. For India means the peasantry and labour and to the extent that we raise them and satisfy their wants will we succeed in our task. And the measure of the strength of our national movement will be the measure of their adherence to it. We can only gain them to our side by our espousing their cause which is really the country’s cause. The Congress has often expressed its goodwill towards them; but beyond that it has not gone. The Congress, it is said, must hold the balance fairly between capital and labour and zamindar and tenant.
But the balance has been and is terribly weighed on one side, and to maintain the status quo is to maintain injustice and exploitation. The only way to right it is to do away with the domination of any one class over another. The All-India Congress Committee accepted this ideal of social and economic change in a resolution it passed some months ago in Bombay. I hope the Congress will also set its seal on it and will further draw up a programme of such changes as can be immediately put in operation.
In this programme perhaps the Congress as a whole cannot go very far today. But it must keep the ultimate ideal in view and work for it. The question is not one merely of wages and charity doled out by an employer or landlord. Paternalism in industry or in the land is but a form of charity with all its sting and its utter incapacity to root out the evil. The new theory of trusteeship, which some advocate, is equally barren. For trusteeship means that the power for good or evil remains with the self-appointed trustee and he may exercise it as he will. The sole trusteeship that can be fair is the trusteeship of the nation and not of one individual or a group. Many Englishmen honestly consider themselves the trustees for India, and yet to what a condition they have reduced our country.
We must decide for whose benefit industry must be run and the land produce food. Today the abundance that the land produces is not for the peasant or the labourer who works on it; and industry’s chief function is supposed to be to produce millionaires. However golden the harvest and heavy the dividends, the mud-huts and hovels and nakedness of our people testify to the glory of the British Empire and of our present social system.
Our economic programme must therefore be based on a human outlook and must not sacrifice man to money. If an industry cannot be run without starving its workers, then the industry must be closed down. If the workers on the land have not enough to eat then the intermediaries who deprive them of their full share must go. The least that every worker in the field or factory is entitled to is a minimum wage which will enable him to live in moderate comfort, and human hours of labour which do not break his strength and spirit.
Our economic programme must therefore be based on a human outlook and must not sacrifice man to money. If an industry cannot be run without starving its workers, then the industry must be closed down. If the workers on the land have not enough to eat then the intermediaries who deprive them of their full share must go. The least that every worker in the field or factory is entitled to is a minimum wage which will enable him to live in moderate comfort, and human hours of labour which do not break his strength and spirit. The All-Parties’ Committee accepted the principle and included it in their recommendations. I hope the Congress will also do so and will in addition be prepared to accept its natural consequences. Further that, it will adopt the well known demands of labour for a better life, and will give every assistance to organize itself and prepare itself for the day when it can control industry on a cooperative basis.
But industrial labour is only a small part of India, although it is rapidly becoming a force that cannot be ignored. It is the peasantry that cry loudly and piteously for relief and our programme must deal with their present condition. Real relief can only come by a great change in the land-laws and the basis of the present system of land tenure. We have among us many big landowners and we welcome them. But they must realize that the ownership of large estates by individuals, which is the outcome of a state resembling the old feudalism of Europe, is a rapidly disappearing phenomenon all over the world. Even in countries which are the strongholds of capitalism, the large estates are being split up and given to the peasantry who work on them. In India also we have large areas where the system of peasant proprietorship prevails and we shall have to extend this all over the country. I hope that in doing so, we may have the cooperation of some, atleast of the big landowners.
It is not possible for this Congress at its annual session to draw up any detailed economic programme. It can only lay down some general principles and call upon the All India Congress Committee to fill in the details in cooperation with the representatives of the Trade Union Congress and other organizations which are vitally interested in this matter. Indeed, I hope that the cooperation between this Congress and the Trade Union Congress will grow and the two organizations will fight side by side in future struggles.
All these are pious hopes till we gain power, and the real problem therefore before us is the conquest of power. We shall not do so by subtle reasoning or argument or lawyers’ quibbles, but by the forging of sanction to enforce the nation’s will. To that end, this Congress must address itself.
The past year has been one of preparation for us and we have made every effort to reorganize and strengthen the Congress Organization. The results have been considerable and our organization is in a better state today than at any time since the reaction which followed the non-cooperation movement. But our weaknesses are many and are apparent enough. Mutual strife, even within Congress Committees, is unhappily too common and election squabbles drain all our strength and energy. How can we fight a great fight if we cannot get over this ancient weakness of ours and rise above our petty selves? I earnestly hope that with a strong programme of action before the country, our perspective will improve and we will not tolerate this barren and demoralizing strife.
What can this programme be? Our choice is limited, not by our own constitution, which we can change at our will but by facts and circumstances. Article one of our constitution lays down that our methods must be legitimate and peaceful. Legitimate I hope they will always be, for we must not sully the great cause for which we stand, by any deed that will bring dishonour to it and that we may ourselves regret later. Peaceful I should like them to be, for the methods of peace are more desirable and more enduring than those of violence. Violence too often brings reaction and demoralization in its train, and in our country especially it may lead to disruption. It is perfectly true that organized violence rules the world today and it may be that we could profit by its use. But we have not the material or the training for organized violence and individual or sporadic violence is a confession of despair. The great majority of us, I take it, judge the issue not on moral but on practical grounds, and if we reject the way of violence it is because it promises no substantial results.
Any great movement for liberation today must necessarily be a mass movement and mass movement must essentially be peaceful, except in times of organized revolt. Whether we have the non-cooperation of a decade ago or the modern industrial weapon of the general strike, the basis is peaceful organization and peaceful action. And if the principal movement is a peaceful one, contemporaneous attempts at sporadic violence can only distract attention and weaken it.
Any great movement for liberation today must necessarily be a mass movement and mass movement must essentially be peaceful, except in times of organized revolt. Whether we have the non-cooperation of a decade ago or the modern industrial weapon of the general strike, the basis is peaceful organization and peaceful action. And if the principal movement is a peaceful one, contemporaneous attempts at sporadic violence can only distract attention and weaken it. It is not possible to carry on at one and the same time the two movements, side by side. We have to choose and strictly to abide by our choice. What the choice of this Congress is likely to be I have no doubt. It can only choose a peaceful mass movement.
Should we repeat the programme and tactics of the non-cooperation movement? Not necessarily, but the basic idea must remain. Programmes and tactics must be made to fit in with circumstances and it is neither easy nor desirable for this Congress at this stage to determine them in detail. That should be the work of its executive, the All-India Congress Committee. But the principles have to be fixed.
The old programme was one of the three boycotts—Councils, law courts and schools—leading up to refusal of service in the army and non-payment of taxes. When the national struggle is at its height, I fail to see how it will be possible for any person engaged in it to continue in the courts or the schools. But still I think that it will be unwise to declare a boycott of the courts and schools at this stage.
The boycott of the Legislative Councils has led to much heated debate in the past and this Congress itself has been rent in twain over it. We need not revive that controversy, for the circumstances today are entirely different. I feel that the step the Congress took some years ago to permit Congressmen to enter the Councils was an inevitable step and I am not prepared to say that some good has not resulted from it. But we have exhausted that good and there is no middle course left today between boycott and noncooperation. All of us know the demoralization that these sham legislatures have brought in our ranks and how many of our good men, their committees and commissions lured away. Our workers are limited in number and we can have no mass movement unless they concentrate on it and turn their backs to the palatial Council Chambers of our Legislatures. And if we declare for independence, how can we enter the Councils, and carry on our humdrum and profitless activities there? No programme or policy can be laid down for ever, nor can this Congress bind the country or even itself to pursue one line of action indefinitely. But today I would respectfully urge the Congress that the only policy in regard to the Council is a complete boycott of them. The All-India Congress Committee recommended this course in July last and the time has come to give effect to it.
This boycott will only be a means to an end. It will release energy and divert attention to the real struggle which must take the shape of the nonpayment of taxes, where possible, with the cooperation of the labour movement, general strikes. But nonpayment of taxes must be well organized in specific areas, and for this purpose the Congress should authorize the All India Congress Committee to take the necessary action, wherever and whenever it considers desirable.
I have not so far referred to the constructive programme of the Congress. This should certainly continue but the experience of the last few years shows us that by itself it does not carry us swiftly enough. It prepares the ground for future action and ten years’ silent work is bearing fruit today. In particular we shall, I hope, continue our boycott of foreign cloth and the boycott of British goods.
Our programme must, therefore, be one of political and economic boycott. It is not possible for us, so long as we are actually independent, and even then completely, to boycott another country wholly or to sever all connection with it. But our endeavour must be to reduce all points of contact with the British Government and to rely on ourselves. We must also make it clear that India will not accept responsibility for all the debts that England has piled on her. The Gaya Congress repudiated liability to pay those debts and we must repeat this repudiation and stand by it. Such of India’s public debt as has been used for purposes beneficial to India we are prepared to admit and pay back. But we wholly deny all liability to pay back the vast sums which have been raised, so that India may be held in subjection and her burdens may be increased. In particular the poverty stricken people of India cannot agree to shoulder the burden of the wars fought by England to extend her domain and consolidate her position in India. Nor can they accept the many concessions lavishly bestowed without any proper compensation on foreign exploiters.
I have not referred so far to the Indians overseas and I do not propose to say much about them. This is not from any want of fellow-feeling with our brethren in East Africa or South Africa or Fiji or elsewhere, who are bravely struggling against great odds. But their fate will be decided in the plains of India and the struggle we are launching into is as much for them as for ourselves.
For this struggle, we want efficient machinery. Our Congress Constitution and organization have become too archaic and slow moving, and are illsuited to times of crisis. The times of great demonstrations are past. We want quiet and irresistible action now, and this can only be brought about by the strictest discipline in our ranks. Our resolutions must be passed in order to be acted upon. The Congress will gain in strength, however small its actual membership may become, if it acts in a disciplined way. Small, determined minorities have changed the fate of nations. Mobs and crowds can do little. Freedom itself involves restraint and discipline and each one of us will have to subordinate himself to the larger good.
The Congress represents no small minority in the country and though many may be too weak to join it or to work for it, they look to it with hope and longing to bring them deliverance. Ever since the Calcutta resolution, the country has waited with anxious expectation for this great day when this Congress meets. None of us can say what and when we can achieve. We cannot command success. But success often comes to those who dare and act; it seldom goes to the timid who are ever afraid of the consequences. We play for high stakes; and if we seek to achieve great things it can only be through great dangers. Whether we succeed soon or late, none but ourselves can stop us from high endeavour and from writing a noble page in our country’s long and splendid history.
Success often comes to those who dare and act; it seldom goes to the timid who are ever afraid of the consequences. We play for high stakes; and if we seek to achieve great things it can only be through great dangers. Whether we succeed soon or late, none but ourselves can stop us from high endeavour and from writing a noble page in our country’s long and splendid history.
We have conspiracy cases going on in various parts of the country. They are ever with us. But the time has gone for secret conspiracy. We have now an open conspiracy to free this country from foreign rule, and you comrades, and all our countrymen and countrywomen are invited to join it. But the rewards that are in store for you are suffering and prison and you will have done your little bit for India, the ancient, but ever young, and have helped a little in the liberation of humanity from its present bondage.

M. Singaravelu
I think this conference is the first of its kind in the whole of India. One can boldly assert that this conference will bring good to the country and people. Unfortunately some people, out of ignorance, have ridiculed this conference. As usual, theists indulge in slander. The bureaucrats try to indulge in repression under some pretext or other. But this is not a new occurrence. In the past all progressive movements have been persecuted and ridiculed.
Not content with ridiculing the progressive movement, this mad and ignorant world has always tried to stop the spread of scientific knowledge. Ingersol, the famous atheist of America was not taken note of during his lifetime and was even ridiculed. But now his birth anniversary is being celebrated in America. Bradlaugh, the British atheist, was put behind bars during his lifetime. Now what happens in Britain? Commemoration meetings in honour of Bradlaugh are being held in Britain. I am sure in due course still bigger conferences of this kind would be held in this country. It is quite likely that people may forget the names of the atheists but their ideas will remain forever in their minds.
Atheism is an ancient doctrine which originated and developed side by side with theism. When the concept of God was ushered in, alongside came the doctrine of ‘no-God’. Till the time man developed his faculty to speak, he was not aware of any God. Some of the primitive tribesmen have confessed their ignorance about God, and can aptly be called ‘primitive atheists’.
Atheism is an ancient doctrine which originated and developed side by side with theism. When the concept of God was ushered in, alongside came the doctrine of ‘no-God’. Till the time man developed his faculty to speak, he was not aware of any God. Some of the primitive tribesmen have confessed their ignorance about God, and can aptly be called ‘primitive atheists’.
In this connection it is really interesting to note the history of religion. Every religion had proclaimed that people belonging to the other religions were atheists. A non-Hindu is an atheist to a Hindu. To a Muslim any non- Muslim is an atheist. Likewise, many more people were termed as atheists. Hence, I would like to say one should really be proud to be an atheist as he is not only non-religious but also does not accept a belief in God.
As the word (God) was man’s own creation, he began to build houses (temples) for his God. Just as he respected his superiors and elders, he began to respect his God. What he did to entertain himself like music, dance, rituals, feasts, he offered to his God. Thus, God advanced as man advanced.
Some shrewd men of those days found an easy way to life and this paved the way for replacing the word with an idol. To make man live perpetually in fear of God, these men did everything possible and thus priesthood came into existence. These priests lived and thrived on the fear and ignorance of men. Thus around the single word ‘God’ the entire edifice of religious and philosophical system of rituals and prayers were built. In the course of history, many beliefs have become obsolete and I am sure that this belief, namely, theism too would become obsolete in due course.
The first and most dangerous affect of theism is that it saps the initiative of man. Ignorance take deep roots in him. People are prevented from acquiring scientific knowledge. Theism is not only a negative evil; it is positively harmful to the people.
The first and most dangerous affect of theism is that it saps the initiative of man. Ignorance take deep roots in him. People are prevented from acquiring scientific knowledge. Theism is not only a negative evil; it is positively harmful to the people. Whatever may be the future of God, we can never forget and forgive his past. It is only atheism that instills confidence in man. It is only atheism which proclaims that social and economic inequalities are only manmade. Hence, it goads man to seek out ways of removing obstacles in the way of progress. It is only atheism that proclaims to man: ‘Man, be a man. You alone can convert this earth into a paradise.’
Comrades, crucial battles are ahead of us. We cannot rest on our laurels now. Though it is put on defence, theism has not been completely routed. Power, money, propaganda, still side with theism. Further, a majority of people, out of ignorance still remain with theism and we have to redeem them. Theism alongwith power and money may over and again attempt to bar the growth and development of human initiative. A concrete example is the development of Hitlerism and fascism. Religious beliefs and other ageold obscurantist ideas are thrust down the throats of people. This is a dangerous trend. Take again some of the views expressed by Gandhiji. He is openly advocating theism. Further, he is crying to make some readjustment in the caste system, to reform it. In our view these are against the principles of atheism. The so-called removal of untouchability is a mere device to strengthen religious beliefs among the people. The untouchables numbering about six crores are economically poor and downtrodden. What they need is neither God or religion. They need a meal a day and an opportunity to earn a decent living.
Comrades, crucial battles are ahead of us. We cannot rest on our laurels now. Though it is put on defence, theism has not been completely routed. Power, money, propaganda, still side with theism. Further, a majority of people, out of ignorance still remain with theism and we have to redeem them. Theism alongwith power and money may over and again attempt to bar the growth and development of human initiative.
However, there is another danger ahead. The Hindu Mahasabha, the Sanatanis, Muslim communalists, etc., are still striving hard to capture the legislative assembly so that theism can be enthroned. These are the worst reactionaries in this unfortunate land. Beware comrades, not to lose this opportunity for contesting and capturing every seat in every village and panchayat, in every taluk and district board. Fearlessly expose the sham of casteism and oppression. Dethrone ignorance and theism. Please, enthrone atheism and socialism in its place.
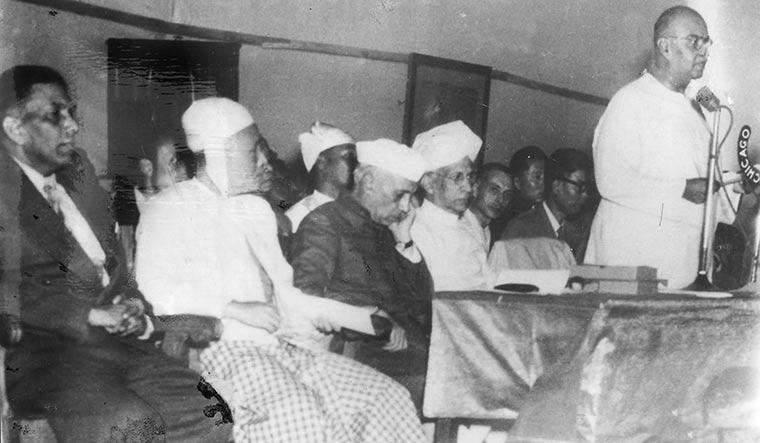

Syama Prasad Mookerjee
Sir, since yesterday we have been discussing the motions of no-confidence under circumstances, which perhaps have no parallel in the deliberations of any Legislature in any part of the civilized world. What happened in Calcutta is without a parallel in modern history. St Bartholomew’s Day of which history records some grim events of murder and butchery pales into insignificance compared to the brutalities that were committed in the streets, lanes and bye-lanes of this first city of British India. We have been discussing, Sir, as to the genesis of these disturbances. Time will not permit me to go through the detailed history and course of events during the last few years.
But let me say this that what has happened is not the result of a sudden explosion, but it is the culmination of an administration, inefficient, corrupt and communal, which has disfigured the life of this great Province. But so far as the immediate cause is concerned, rightly reference has been made by members belonging to the Muslim League and also to the Opposition that we have to look to the resolution that was passed at Bombay at the all-India session of the Council of the Muslim League. Now what happened there? It is said, on behalf of the Muslim League that the Cabinet Mission proved faithless to Muslim interests and thereby created a situation which had no parallel in the history of Anglo-Muslim relationship in this country. What did actually the Cabinet Mission do? The Muslim League, the spoilt and pampered child of the British imperialists for the last thirty years, was disowned for the first time by the British Labour Government…(loud noise from the government benches)…I know it that members when they hear the bitter truth, can hardly repress their feelings. Sir, the fact remains that the old policy of the British Government of no advancement without a Congress-Muslim League agreement was for the first time given up in I946…(loud cries from the government benches)…I have only stated the fact and I do not make any comment on it and still my friends become impatient immediately. Now, the fact remains that the Muslim League was bypassed and the Interim Government has been formed at the Centre. Supposing Mr Jinnah had been asked to form the Interim Government without the Congress, would my friends belonging to the Muslim League have then blamed the government for having betrayed the interests of the Hindu community?
But let me say this that what has happened is not the result of a sudden explosion, but it is the culmination of an administration, inefficient, corrupt and communal, which has disfigured the life of this great Province. But so far as the immediate cause is concerned, rightly reference has been made by members belonging to the Muslim League and also to the Opposition that we have to look to the resolution that was passed at Bombay at the all-India session of the Council of the Muslim League.
Sir, what happened after the Bombay resolution? I have before me a summary of the speeches delivered by distinguished spokesmen on behalf of the Muslim League in every part of India and although it was said that the Direct Action Day itself was not the day for commencing direct action, it was at the same time pointed out that the war had begun, the days of peace and compromise were over and now the jehad … (A member from the Government Benches: Against whom?) War against everyone who did not accept Pakistan. That has been made abundantly clear.
I would ask my friends not to misunderstand me. I am trying to put in brief their point of view as I would ask them also to appreciate our point of view. We are like poles asunder. You say you will plunge the country Pakistan by any means whatsoever. These two points of view are irreconcilable and what I am now telling the House is this that the members speaking on behalf of the Muslim League did not mince matters. Muslim leaders want Civil War. Only a pattern of civil war, according to Mr Jinnah, was witnessed in this very city of Calcutta, but whether civil war will ultimately help Muslims to get Pakistan or not is a matter that remains yet to be seen. It is said that British Imperialists are against the Muslim League. Why talk rot in this way? Who gave you separate electorate and communal award? Who is helping the Sind ministry to remain in power? Is not the Governor a British Governor? Are not the three European members of the Sind Assembly British members of that House? Are they not trying their level best somehow to keep the Muslim League in power and not allow the Congress to go to office although among the Indian members they are in a majority?
Now, Sir, I shall leave this aside. I shall not refer to the detailed speeches which have been delivered by the Muslim League leaders barring one or two illustrative remarks. When Mr Jinnah was confronted at a preconference in Bombay on the 31st July and was asked whether direct action involved violence or non-violence, his cryptic reply was ‘I am not going to discuss ethics’. (The Hon’ble Mr Muhammad Ali: Good.) But Khwajah Nazimuddin was not so good. He came out very bluntly in Bengal and he said that Muslims did not believe in non-violence at all, Muslims knew what direct action meant and there were one hundred and one ways in which this was made clear by responsible League leaders. One said in the Punjab that the zero hour had struck and that the war had begun. All this was followed by a series of articles and statements which appeared in the columns of newspapers— the Morning News, the Star of India, and the Azad. If you read those documents, particularly I would ask my friend Mr Ispahani if he reads those documents, I do not know whether he had learnt Bengali yet, if not, for his benefit a translation can be made of the Bengali article in Azad, he will be able to find out that there was nothing but open and direct incitement to violence. Hatred of Hindus and jehad on the Hindu were declared in highly charged language. That was the background. I am not going to quote the papers, for I have not the time. You have read them and the general Muslim public have acted according to the instructions.
Now, so far as the later events are concerned, what happened on the 16th of August. What were the preparations made? Mr Ispahani says that they were taken unaware. In the Morning News on the 16th there appeared an announcement on behalf of the ‘Pakistan’ Ambulance Corps and there full instructions were given as to how the Ambulance Corps was to act—mind you, Sir, this was done before the troubles started. This ‘Pakistan Ambulance Corps’ was to be utilized in different parts of the city; they were to go out in batches, cars and officers ‘would be available’ and from the 17th morning announcement was to be made every hour as regards the patients who were to be found in the different hospitals of Calcutta. This was announced before any trouble started in Calcutta and Mr Ispahani says there was no preparation. Of course it was sheer bad luck that you allowed this notice, among many kinds of preparations, to be published in the newspapers.
Now, Sir, what happened on the 16th? I shall not refer to the detailed speeches of other members. But I shall certainly hold responsible the Chief Minister of this province who lost his mental balance by saying in Bombay that he was going to declare Bengal to be an independent state. A minister who cannot control his British underling — the Commissioner of Police — is going to make Bengal an independent state! A minister who comes forward and says ‘I am helpless, I could not save the people of the city because the Commissioner of Police would not listen to me’ will declare Bengal an independent state! Now, that was Mr Suhrawardy. He said he was going to carry on a no-rent campaign in this province. He was going to disobey law and order. His speech before the Legislative Council goes to show that he knew fully well that troubles were ahead. If you analyse his speech it will appear that he knew that troubles were brewing and he said he wanted to be as careful as possible.
Now, Sir, what happened on the 16th? I shall not refer to the detailed speeches of other members. But I shall certainly hold responsible the Chief Minister of this province who lost his mental balance by saying in Bombay that he was going to declare Bengal to be an independent state. A minister who cannot control his British underling — the Commissioner of Police — is going to make Bengal an independent state!
I am not raising the question in this debate as to how many Hindus were butchered or how many Muslims were butchered in Bhawanipore, Taltolla, or Watgunge. That is not the issue. The question in issue today is, did government succeed in protecting life and property; not to which community that life and property belonged? Why did government allow so many Muslim lives to be butchered if you look upon Mr Suhrawardy as the great Muslim champion? Why did he allow the entire administration of law and order to collapse in the city? I shall say, Sir, it was a diabolical plan. I say Sir, there was a well-organized plan to make a lightning attack on the city that would take Hindus by surprise, properties were going to be looted and lives were going to be lost. Then Mr Suhrawardy found that he was caught in his own trap when he and others were hit back in their own coin. He could not regain his lost ground and failed to do what his Muslim brethren asked him to do in agony and distress.
I am not raising the question in this debate as to how many Hindus were butchered or how many Muslims were butchered in Bhawanipore, Taltolla, or Watgunge. That is not the issue. The question in issue today is, did government succeed in protecting life and property; not to which community that life and property belonged?
On the 16th, our case is that provocation came from the other side, their case is that provocation came from the Hindu side. That also I am not going to discuss today. Let us leave that for the time being, but let us proceed to the next stage. Mr Suhrawardy said by 12 noon he realized the situation was very bad. Was he not still the Chief Minister of Bengal? What did he do at that time? Why was not the military called out at that time? I have got here a circular issued by the military for the information of its officers and employees in which clear information is given that the military was ready to come out on Friday noon but it was not asked to do so. The civil police failed to protect the life and property as it was expected to do and whenever the military was asked to come out, it came out and it did whatever it could do. But, alas, thousands had been killed meanwhile and crores of rupees looted!
On Friday Mr Suhrawardy knew that trouble had broken out— no matter whether the Hindus were the aggressors or the Muslims were, why did he allow the whole city to be placed at the mercy of goondas, dacoits and murderers? Why did he allow the meeting at all to be held at the maidan in the afternoon over which he presided? He stands charged with the deliberate offence of having played havoc with the life and property of the citizens of this great city, no matter whether they were Hindus or they were Muslims. On Friday night he gave a message to the Associated Press that the condition in the city had improved. Does he remember it? It seems that the Associated Press went to the next day’s newspapers. I would ask my friends to forget for the time being that they belong to the Muslim League. If Mr Suhrawardy says ‘no’, here, Sir, is the statement of Mr H.S. Suhrawardy, Chief Minister of Bengal— I suppose that is the gentleman sitting over there (laughter) interviewed by the Associated Press of India to the effect that the situation was improving. (Uproar) (A voice from the government benches: What paper?) Every newspaper. (Renewed uproar.) I would ask my friends that they must observe the rules of the game and fairplay even in a discussion like this. Why don’t you ask the Chief Minister to explain this?
Mr Speaker, you can certainly look into it. I am not afraid of the truth. Yes, Sir, (Sent the paper to Mr Speaker.) I can produce it to anyone who wants to see it. Now, Sir, Section l44 is supposed to have been promulgated on Friday but was never enforced.
Then on Saturday the curfew order was inaugurated, but neither Section 144 nor the curfew order was enforced. How is it that in spite of Section 144 and the curfew order people were moving about committing loot and plunder, and murder even? How is it that within a stone’s throw, Mr Ispahani has pointed out, from Lalbazar police station shops were looted, people were murdered and all sorts of offences were committed without the Police moving an inch?
Of course, you are responsible. If you have got the guts to say that you are not responsible, let us know that. Now, Sir, that was on the 16th and 17th August. Later on what happened? Mr Suhrawardy knows it very well that he was telling a double-faced lie. On the 23rd he issued a broadcast message, a message of peace for the people of Bengal and within half an hour of that he sent out a special message for the foreign press through foreign correspondents and the things which are mentioned in that document are entirely different from the broadcast message which he issued to the people of Bengal. Can he deny that? (A voice from the Government Benches: That is obvious). He has stated that the Hindus have started the riot. (The Hon’ble Mr H.S. Suhrawardy: Certainly.) He has said that it is the Hindus, who are to blame. He said it was the British Government which was to blame. Say ‘certainly’ (laughter) and lastly, he said that he cannot yet tell what will happen in future if the Interim Government continues in office. Now, Sir, if that is the remark which he wanted to make on that day what was the use of his appealing to the people of Bengal for peace and harmony and saying ‘I have kept an open mind and I would like Hindus and Muslims to work together’. Can history give us a better example of a double-faced minister?
Sir, there are two matters here which may be mentioned. Mr Suhrawardy said that he could not control the Commissioner of Police because he was not under his orders. I shall give you, Sir, one instance out of many which are available from which it will appear how Mr Suhrawardy interfered with the administration of the police offices in a manner which was unworthy of any Home Minister of any Province. In the Park Street police station about seven goondas were taken by a European Inspector on Sunday evening. Sir, that is the remark which Mr Suhrawardy has made namely, ‘I am sorry you are a goonda then.’ I do not know who they are. These persons were found with looted properties. If Mr Suhrawardy says that Muslim gentlemen took away looted properties I shall bow down my head to him, but if he says that I am a goonda then I too can say that he is the best goonda that is available not only in this Province but throughout the world.
(Uproar)
Sir, I shall withdraw it as soon as Mr Suhrawardy withdraws what he has said about me. (Cries of ‘withdraw, withdraw’ from the government benches). Let him withdraw first, what he first has said about me.
Now I withdraw too. Now, Sir, let me pass on. So far as the Park Street incident is concerned, the important point is that goondas or gentlemen whoever they were, seven Muslims who were found in possession of looted properties were brought into Park Street police-station by a European Inspector. Within ten minutes Mr H.S. Suhrawardy appears on the scene. He gets these persons released. It is on record. Let him deny that. (The Hon’ble Mr H.S. Suhrawardy: Yes). (Cries of ‘shame, shame’ from Congress benches.) Then he comes back (Mr H.S. Suhrawardy: Oh! no). This is the way, Sir, in which Mr Suhrawardy has behaved. This is one instance I am giving. (Cries of ‘you have cooked it’ from government benches). No, I have not cooked it. He himself has admitted it.
Then, Sir, the Muslim League party wanted 500 gallons of petrol from the Bengal Government. That was not granted, but petrol coupons were issued in the name of individual ministers — general coupons — 100 gallons being issued in the name of the Chief Minister. Evidence is available that these coupons were used by lorries moving in the streets of Calcutta on those fateful days. That is how arrangements were being made under the very nose of the Home Department over which Mr Suhrawardy was presiding. Can Mr Suhrawardy deny that he himself went to Howrah accompanied by some Muslim League leaders, met local officers in authority there, and had chastized and taken them to task because Muslims were not protected there? Can he deny that? Did Mr Suhrawardy give in any place or at any time the same sort of protection to the suffering Hindus. (The Hon’ble Mr H.S. Suhrawardy: Certainly). Now, Sir, it is quite clear that at least I have said some home truths which have made my friends opposite angry and impatient.
Sir, they, these ministers, have taken oath of allegiance to the British Crown and they are responsible for the life and property of all alike. My friend, Mr Muhammad Ali, admitted this very candidly when the adjournment motion was not allowed to be taken up in this House. Mr Suhrawardy is a great Muslim League leader and he owes his allegiance to the Muslim League. The Muslim League rightly or wrongly ordered that if something does not happen to its liking, it was going to resort to direct action. One cannot serve two masters. Sir, it has been proved beyond doubt that Mr Suhrawardy and his other Ministers are unable to administer the affairs of this Province impartially and efficiently. They have failed hopelessly and wretchedly and on that ground alone they are not fit to occupy offices for a single moment (Interruptions).
Sir, it is not in Calcutta alone that atrocities were committed in a large scale, but we find that troubles are spreading now in the whole of Bengal. The information which is coming from different parts of Bengal would make one shudder to think as to what will happen to this province. These gentlemen, the ministers over there, should not remain in charge of the affairs of this province even a day longer.
Sir, it is not in Calcutta alone that atrocities were committed in a large scale, but we find that troubles are spreading now in the whole of Bengal. The information which is coming from different parts of Bengal would make one shudder to think as to what will happen to this province. These gentlemen, the ministers over there, should not remain in charge of the affairs of this province even a day longer. (Interruptions) If they remain in office the future would be darker still. (Interruptions) The Council of Action of the All-India Muslim League has ordered that preparations have to be made for giving effect to the Direct Action Program. Already Muslim League leaders from the Punjab, North-West Frontier Province and also Sind have openly declared that they are ready with their scheme which can be put into operation at 24 hours’ notice. Am I to believe that the Muslim League in Bengal which is a stronghold of Mr Jinnah’s Muslim League is not similarly prepared to give effect to the order of the Muslim League when the occasion demands it? In other words, my charge is that the present Ministry is utilizing the government machinery for the purpose of launching upon a Direct Action scheme. (The Hon’ble Mr H.S. Suhrawardy: No). Mr Suhrawardy is playing a dual role and this dual role of Mr Suhrawardy and those who are supporting him has got to be exposed and brought to an end in the interest of peace and tranquility.
Why does not the Chief Minister get the reports of the Commissioner of Police through the Criminal Investigation Department as regards some meetings which took place in the city? Mr Suhrawardy has perhaps got the proceedings confidentially of the meetings which were held in the cities where League leaders were invited to attend for the purpose of preparing scheme for direct action. If he has got any report about what happened on the 16th, he will find that even when the Calcutta maidan meeting was being held, over which Mr Suhrawardy presided, disturbances had broken out in several places. Now what happened in that meeting? Was there then any CID officer present taking down notes? Where are those notes?
Sir, it was an astonishing fact that a gun shop within 2 minutes walk from the Government House had been looted. Not a single policeman turned up in the streets to control the situation in any part of the city. It will not help merely making the Commissioner of Police a scapegoat, it is suggested that the city had been ablaze in so many places that the Commissioner of Police did not know how to act. But surely Mr Suhrawardy knew how and when to act. (The Hon’ble Mr H.S. Suhrawardy: Yes, yes). Mr Suhrawardy says that he knew and we also know when he acted. If he had failed without making any effort, then he is charged with criminal negligence and if he failed in spite of efforts, he is certainly inefficient and worthless, and he should not be kept in that position any longer. There is no place for him in the ministry.
Sir, there is one point which I would like to say with regard to the Britishers in this House. My friends are remaining neutral. I cannot understand this attitude at all. In a situation such as this they must decide if the ministry was right or the ministry was wrong. If the ministry was right, support them and if the ministry was wrong, you should say so boldly and not remain neutral merely sitting on the fence which shows signs of abject impotence (Laughter).
If a single Britisher, man or woman or a child, had been strong enough they would have thrown this ministry out of office without hesitation, but because no Britisher was touched so they can take an impartial and neutral view! Are they so sure they will be left untouched next time? There is no question of partiality or impartiality here. The present administration has failed and it must come to an end. Anyone who remains neutral is an aider and abettor.
My friend, Mr Gladding, said that luckily none of his people were injured. It is true, Sir, but that is a statement which makes me extremely sorry. If a single Britisher, man or woman or a child, had been strong enough they would have thrown this ministry out of office without hesitation, but because no Britisher was touched so they can take an impartial and neutral view! Are they so sure they will be left untouched next time? There is no question of partiality or impartiality here. The present administration has failed and it must come to an end. Anyone who remains neutral is an aider and abettor.
I would ask my friends, what about the future. Pakistan will not be accepted under any circumstance. (Mr Fazlur Rahman: It will be accepted). Mr Suhrawardy said in Bombay after the 16th of August, ‘When a nation fights against another nation I cannot guarantee civilized conduct.’ If you are a nation fighting against us, another nation, if that is the attitude of my friends on the other side, then they cannot remain in office any longer. (Cries of ‘Hear, hear’ from the Opposition Benches). Mr Suhrawardy must realize that his office is meant for the good of the entire people of Bengal irrespective of caste, creed and religion, and not for his own so-called ‘nation’. I would say, Sir, that is an abject treachery to the great responsibility that rests on Mr Suhrawardy, as Premier (Interruptions).
Apparently I said many good things, otherwise my friends would not be so jubilant. The Chief Minister was dancing the other day on the polished floor of a Delhi Hotel and I have made my friends dance on the floor of this House. I will now say a few words in connection with the future. What about the future? My friends, the Muslims, say that they constitute 25 percent of India’s population, and that is so big a minority that they will never agree to live under 75 percent Hindu domination. Now if that is their honest and genuine point of view how can they expect that 45 percent of the Hindu population of this Province will ever agree to live under a Constitution where that particular nation represented by Muslims, constituting only of 55 percent, will alone dominate? (The Hon’ble Mr Shamsuddin Ahmed: That is how the trouble began). I will not today enter into controversies as regards the real population of Bengal. I claim it that if a proper census is taken even today the Hindus will not be in a minority but that question cannot be settled by argument from one side or the other. My Muslim friends who are well-organized under the banner of the Muslim League have got to realize that if Bengal is to be ruled peacefully it can be done only with the willing cooperation of the two communities. I am not talking of all India politics for the time being. (The Hon’ble Mr Shamsuddin Ahmed: Why not? What has happened to all India politics?) I would make this appeal to my friends that a choice has to be made by the Hindus and the Muslims together. There is no way out of it because what we witnessed in Calcutta was not an ordinary communal riot: its motive was political, but things may become even far more serious and drastic in the days, weeks and months to come. Now, if the Muslims of Bengal under the leadership of the Muslim League feel that they can exterminate the Hindus, that is a fantastic idea which can never be given effect to: three and a half crores can never exterminate three crores nor can three crores exterminate three and a half crores.
Sir, if it is said that civil war will break out throughout India, will that help anyone, will that help, in particular, 25 percent. Muslims throughout India as against 75 percent of Hindus and other non-Muslims. It is not a question of threat at all; it is a question of facing a stern reality. Either we have to fight or we have to come to some settlement. The settlement cannot be reached so long as you say that one community will dominate over the other, but it can only be reached by a plan which will enable the vast majority of Hindus and Muslims to live under circumstances which will give freedom and peace to the common man.
Now, Sir, if it is said that civil war will break out throughout India, will that help anyone, will that help, in particular, 25 percent. Muslims throughout India as against 75 percent of Hindus and other non-Muslims. It is not a question of threat at all; it is a question of facing a stern reality. Either we have to fight or we have to come to some settlement. The settlement cannot be reached so long as you say that one community will dominate over the other, but it can only be reached by a plan which will enable the vast majority of Hindus and Muslims to live under circumstances which will give freedom and peace to the common man. After all, forget not who suffered most during the Calcutta Killing. It as mainly the poorer people, both amongst the Hindus and the Muslims. Ninety percent of them were poor and innocent and if the leaders lose their heads and go creating a situation which they cannot ultimately control, the time will soon come when the common man will turn round and crush the leaders instead of being themselves crushed. It is therefore vitally necessary that this false and foolish idea of Pakistan or Islamic rule has to be banished for ever from your head. In Bengal we have got to live together. We say as a condition precedent this ministry must go. Only then can we create a state of affairs which will make it possible to build a future Bengal which will be for the good of all, irrespective of any caste, creed, or community.

Jinnah speaking at the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan on 14 August 1947
Mr President, Ladies and Gentlemen!
I cordially thank you, with the utmost sincerity, for the honor you have conferred upon me — the greatest honour that is possible for this Sovereign Assembly to confer — by electing me as your first President. I also thank those leaders who have spoken in appreciation of my services and their personal references to me. I sincerely hope that with your support and your cooperation we shall make this Constituent Assembly an example to the world. The Constituent Assembly has got two main functions to perform. The first is the very onerous and responsible task of framing our future Constitution of Pakistan and the second is functioning as a full and complete sovereign body as the Federal Legislature of Pakistan. We have to do the best we can in adopting a provisional constitution for the Federal Legislature of Pakistan. You know really that not only we ourselves are wondering but, I think, the whole world is wondering at this unprecedented cyclonic revolution which has brought about the plan of creating and establishing two independent sovereign dominions in this subcontinent. As it is, it has been unprecedented; there is no parallel in the history of the world. This mighty subcontinent with all kinds of inhabitants has been brought under a plan which is titanic, unknown, unparalleled. And what is very important with regard to it is that we have achieved it peacefully and by means of an evolution of the greatest possible character.
Dealing with our first function in this Assembly, I cannot make any well considered pronouncement at this moment, but I shall say a few things as they occur to me. The first and the foremost thing that I would like to emphasize is this: Remember that you are now a sovereign legislative body and you have got all the powers. It, therefore, places on you the gravest responsibility as to how you should take your decisions. The first observation that I would like to make is this: You will no doubt agree with me that the first duty of a government is to maintain law and order, so that the life, property and religious beliefs of its subjects are fully protected by the state.
Remember that you are now a sovereign legislative body and you have got all the powers. It, therefore, places on you the gravest responsibility as to how you should take your decisions. The first observation that I would like to make is this: You will no doubt agree with me that the first duty of a government is to maintain law and order, so that the life, property and religious beliefs of its subjects are fully protected by the state.
The second thing that occurs to me is this: One of the biggest curses from which India is suffering — I do not say that other countries are free from it, but, I think, our condition is much worse — is bribery and corruption. That really is a poison. We must put that down with an iron hand and I hope that you will take adequate measures as soon as it is possible for this Assembly to do so.
Black-marketing is another curse. Well, I know that black-marketeers are frequently caught and punished. Judicial sentences are passed or sometimes fines only are imposed. Now you have to tackle this monster which today is a colossal crime against society, in our distressed conditions, when we constantly face shortage of food and other essential commodities of life. A citizen who does black-marketing commits, I think, a greater crime than the biggest and most grievous of crimes. These black-marketeers are really knowing, intelligent and ordinarily responsible people, and when they indulge in black-marketing, I think they ought to be very severely punished, because they undermine the entire system of control and regulation of foodstuffs and essential commodities, and cause wholesale starvation and want and even death.
The next thing that strikes me is this: Here again it is a legacy which has been passed on to us. Alongwith many other things, good and bad, has arrived this great evil—the evil of nepotism and jobbery. This evil must be crushed relentlessly. I want to make it quite clear that I shall never tolerate any kind of jobbery, nepotism or any influence directly or indirectly brought to bear upon me. Whenever I will find that such a practice is in vogue or is continuing anywhere, low or high, I shall certainly not countenance it.
Now, if we want to make this great State of Pakistan happy and prosperous we should wholly and solely concentrate on the well-being of the people, and especially of the masses and the poor. If you will work in cooperation, forgetting the past, burying the hatchet, you are bound to succeed. If you change your past and work together in a spirit that every one of you, no matter to what community he belongs, no matter what relations he had with you in the past, no matter what is his colour, caste or creed, is first, second and last a citizen of this state with equal rights, privileges and obligations, there will be no end to the progress you will make.
I know there are people who do not quite agree with the division of India and the partition of the Punjab and Bengal. Much has been said against it, but now that it has been accepted, it is the duty of every one of us to loyally abide by it and honourably act according to the agreement which is now final and binding on all. But you must remember, as I have said, that this mighty revolution that has taken place is unprecedented. One can quite understand the feeling that exists between the two communities wherever one community is in majority and the other is in minority. But the question is, whether it was possible or practicable to act otherwise than what has been done. A division had to take place. On both sides, in Hindustan and Pakistan, there are sections of people who may not agree with it, who may not like it, but in my judgment there was no other solution and I am sure future history will record its verdict in favour of it. And what is more, it will be proved by actual experience as we go on that it was the only solution of India’s constitutional problem. Any idea of a united India could never have worked and in my judgment it would have led us to terrific disaster. May be that view is correct; may be it is not; that remains to be seen. All the same, in this division it was impossible to avoid the question of minorities being in one dominion or the other. Now that was unavoidable. There is no other solution. Now what shall we do? Now, if we want to make this great State of Pakistan happy and prosperous we should wholly and solely concentrate on the well-being of the people, and especially of the masses and the poor. If you will work in cooperation, forgetting the past, burying the hatchet, you are bound to succeed. If you change your past and work together in a spirit that every one of you, no matter to what community he belongs, no matter what relations he had with you in the past, no matter what is his colour, caste or creed, is first, second and last a citizen of this state with equal rights, privileges and obligations, there will be no end to the progress you will make.
I cannot emphasize it too much. We should begin to work in that spirit and in course of time all these angularities of the majority and minority communities, the Hindu community and the Muslim community—because even as regards Muslims you have Pathans, Punjabis, Shias, Sunnis, and so on and among the Hindus you have Brahmins, Vaishnavas, Khatris, also Bengalees, Madrasis, and so on—will vanish. Indeed if you ask me this has been the biggest hindrance in the way of India to attain the freedom and independence and but for this we would have been free peoples long, long ago. No power can hold another nation, and specially a nation of 400 million souls in subjection; nobody could have conquered you, and even if it had happened, nobody could have continued its hold on you for any length of time but for this. Therefore, we must learn a lesson from this. You are free; you are free to go to your temples, you are free to go to your mosques or to any other place of worship in this State of Pakistan. You may belong to any religion or caste or creed—that has nothing to do with the business of the state. As you know, history shows that in England, conditions some time ago, were much worse than those prevailing in India today. The Roman Catholics and the Protestants persecuted each other. Even now there are some states in existence where there are discriminations made and bars imposed against a particular class. Thank God, we are not starting in those days. We are starting in the days when there is no discrimination, no distinction between one community and another, no discrimination between one caste or creed and another. We are starting with this fundamental principle that we are all citizens and equal citizens of one state. The people of England in course of time had to face the realities of the situation and had to discharge the responsibilities and burdens placed upon them by the government of their country and they went through that fire step by step. Today, you might say with justice that Roman Catholics and Protestants do not exist; what exists now is that every man is a citizen, an equal citizen of Great Britain and they are all members of the Nation.
Now, I think we should keep that in front of us as our ideal and you will find that in course of time Hindus would cease to be Hindus and Muslims would cease to be Muslims, not in the religious sense, because that is the personal faith of each individual, but in the political sense as citizens of the state. Well, gentlemen, I do not wish to take up any more of your time and thank you again for the honour you have done to me. I shall always be guided by the principles of justice and fairplay without any, as is put in the political language, prejudice or ill-will, in other words, partiality or favouritism. My guiding principle will be justice and complete impartiality, and I am sure that with your support and cooperation, I can look forward to Pakistan becoming one of the greatest nations of the world.
Now, I think we should keep that in front of us as our ideal and you will find that in course of time Hindus would cease to be Hindus and Muslims would cease to be Muslims, not in the religious sense, because that is the personal faith of each individual, but in the political sense as citizens of the state.
I have received a message from the United States of America addressed to me. It reads:
I have the honour to communicate to you, in Your Excellency’s capacity as President of the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan, the following message which I have just received from the Secretary of State of the United States:
On the occasion of the first meeting of the Constituent Assembly for Pakistan, I extend to you and to the members of the Assembly, the best wishes of the Government and the people of the United States for the successful conclusion of the great work you are about to undertake.
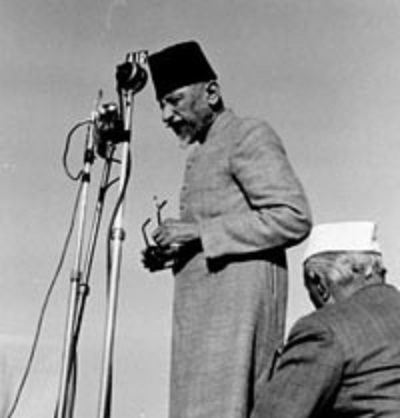

Maulana Abul Kalam Azad
My brethren,
You know what has brought me here today. This congregation at Shahjahan’s historic mosque is not an unfamiliar sight for me. Here, I have addressed you on several previous occasions. Since then we have seen many ups and downs. At that time, instead of weariness, your faces reflected serenity, and your hearts, instead of misgivings, exuded confidence. The uneasiness on your faces and the desolation in your hearts that I see today, reminds me of the events of the past few years.
Do you remember? I hailed you, you cut off my tongue; I picked my pen, you severed my hand; I wanted to move forward, you broke off my legs; I tried to run, and you injured my back. When the bitter political games of the last seven years were at their peak, I tried to wake you up at every danger signal. You not only ignored my call but revived all the past traditions of neglect and denial. As a result the same perils surround you today, whose onset had previously diverted you from the righteous path.
Today, mine is no more than an inert existence or a forlorn cry; I am an orphan in my own motherland. This does not mean that I feel trapped in the original choice that had made for myself, nor do I feel that there is no room left for my ashiana (nest). What it means is that my cloak is weary of your impudent grabbing hands. My sensitivities are injured, my heart is heavy. Think for one moment. What course did you adopt? Where have you reached, and where do you stand now? Haven’t your senses become torpid? Aren’t you living in a constant state of fear? This fear is your own creation, a fruit of your own deeds.
Today, mine is no more than an inert existence or a forlorn cry; I am an orphan in my own motherland. This does not mean that I feel trapped in the original choice that had made for myself, nor do I feel that there is no room left for my ashiana (nest). What it means is that my cloak is weary of your impudent grabbing hands. My sensitivities are injured, my heart is heavy.
It was not long ago when I warned you that the two-nation theory was death-knell to a meaningful, dignified life; forsake it. I told you that the pillars upon which you were leaning would inevitably crumble. To all this you turned a deaf ear. You did not realize that, my brothers! I have always attempted to keep politics apart from personalities, thus avoiding those thorny valleys. That is why some of my messages are often couched in allusions. The Partition of India was a fundamental mistake. The manner in which religious differences were incited, inevitably, led to the devastation that we have seen with our own eyes. Unfortunately, we are still seeing it at some places.
There is no use recounting the events of the past seven years, nor will it serve any good. Yet, it must be stated that the debacle of Indian Muslims is the result of the colossal blunders committed by the Muslim League’s misguided leadership. These consequences however, were no surprise to me; I had anticipated them from the very start.
Now that Indian politics has taken a new direction, there is no place in it for the Muslim League. Now the question is whether or not we are capable of constructive thinking. For this, I have invited the Muslim leaders of India to Delhi, during the second week of November.
The gloom cast upon your lives is momentary; I assure you we can be beaten by none save our own selves! I have always said, and I repeat it again today; eschew your indecisiveness, your mistrust, and stop your misdeeds. This unique triple-edged weapon is more lethal than the two-edged iron sword which inflicts fatal wounds, which I have heard of.
The gloom cast upon your lives is momentary; I assure you we can be beaten by none save our own selves! I have always said, and I repeat it again today; eschew your indecisiveness, your mistrust, and stop your misdeeds. This unique triple-edged weapon is more lethal than the two-edged iron sword which inflicts fatal wounds, which I have heard of.
Just think about the life of escapism that you have opted for, in the sacred name of Hejrat. Get into the habit of exercising your own brains, and strengthening your own hearts. If you do so, only then will you realize how immature your decisions were.
Where are you going and why? Raise your eyes. The minarets of Jama Masjid want to ask you a question. Where have you lost the glorious pages from your chronicles? Wasn’t it only yesterday that on the banks of the Jamuna, your caravans performed wazu? Today, you are afraid of living here. Remember, Delhi has been nurtured with your blood. Brothers, create a basic change in yourselves. Today, your fear is misplaced as your jubilation was yesterday.
The words coward and frenzy cannot be spoken in the same breath as the word Muslim. A true Muslim can be swayed neither by avarice nor apprehension. Don’t get scared because a few faces have disappeared. The only reason they had herded you in a single fold was to facilitate their own flight. Today, if they have jerked their hand free from yours, what does it matter? Make sure that they have not run away with your hearts. If your hearts are still in the right place, make them the abode of God. Some thirteen hundred years ago, through an Arab ummi, God proclaimed, “Those who place their faith in God and are firm in their belief, no fear for them nor any sorrow.” Winds blow in and blow out: tempests may gather but all this is short-lived. The period of trial is about to end. Change yourselves as if you had never been in such an abject condition.
I am not used to altercation. Faced with your general indifference, however, I will repeat that the third force has departed, and along with it, its trappings of vanity. Whatever had to happen has happened. If your hearts have still not changed and your minds still have reservations, it is a different matter. But, if you want a change, then take your cue from history, and cast yourself in the new mould. Having completed a revolutionary phase, there still remains a few blank pages in the history of India. You can make ourselves worthy of filling those pages, provided you are willing.
Brothers, keep up with the changes. Don’t say, “We are not ready for the change.” Get ready. Stars may have plummeted down but the sun is still shining. Borrow a few of its rays and sprinkle them in the dark caverns of your lives.
Brothers, keep up with the changes. Don’t say, “We are not ready for the change.” Get ready. Stars may have plummeted down but the sun is still shining. Borrow a few of its rays and sprinkle them in the dark caverns of your lives.
I do not ask you to seek certificates from the new echelons of power. I do not want you to lead a life of sycophancy as you did during the foreign rule. I want you to remind you that these bright etchings which you see all around you, are relics of processions of your forefathers. Do not forget them. Do not forsake them. Live like their worthy inheritors, and, rest assured, that if you do not wish to flee from this scene, nobody can make you flee. Come, today let us pledge that this country is ours, we belong to it and any fundamental decisions about its destiny will remain incomplete without our consent.
Today, you fear the earth’s tremors; once you were virtually the earthquake itself. Today, you fear the darkness; once your existence was the epicenter of radiance. Clouds have poured dirty waters and you have hitched up your trousers. Those were none but your forefathers who not only plunged headlong into the seas, but trampled the mountains, laughed at the bolts of lightning, turned away the tornadoes, challenged the tempests and made them alter their course. It is a sure sign of a dying faith that those who had once grabbed the collars of emperors, are today clutching their own throats. They have become oblivious of the existence of God as if they had never believed in Him.
Brothers, I do not have a new prescription for you. I have the same old prescription that was revealed to the greatest benefactor of mankind, the prescription of the Holy Quran: “Do not fear and do not grieve. If you possess true faith, you will gain the upper hand.”
Brothers, I do not have a new prescription for you. I have the same old prescription that was revealed to the greatest benefactor of mankind, the prescription of the Holy Quran: “Do not fear and do not grieve. If you possess true faith, you will gain the upper hand.”
The congregation is now at an end. What I had to say, I have said, briefly. Let me say once again, keep a grip on your senses. Learn to create your own surroundings, your own world. This is not a commodity that I can buy for you from the market-place. This can be bought only from the market-place of the heart, provided you can pay for it with the currency of good deeds.
May God’s grace be on you!
| 2500 BC - Present | |

|
2500 BC - Present |
| Tribal History: Looking for the Origins of the Kodavas | |
| 2200 BC to 600 AD | |

|
2200 BC to 600 AD |
| War, Political Violence and Rebellion in Ancient India | |
| 400 BC to 1001 AD | |

|
400 BC to 1001 AD |
| The Dissent of the ‘Nastika’ in Early India | |
| 600CE-1200CE | |

|
600CE-1200CE |
| The Other Side of the Vindhyas: An Alternative History of Power | |
| c. 700 - 1400 AD | |

|
c. 700 - 1400 AD |
| A Historian Recommends: Representing the ‘Other’ in Indian History | |
| c. 800 - 900 CE | |

|
c. 800 - 900 CE |
| ‘Drape me in his scent’: Female Sexuality and Devotion in Andal, the Goddess | |
| 1192 | |

|
1192 |
| Sufi Silsilahs: The Mystic Orders in India | |
| 1200 - 1850 | |

|
1200 - 1850 |
| Temples, deities, and the law. | |
| c. 1500 - 1600 AD | |

|
c. 1500 - 1600 AD |
| A Historian Recommends: Religion in Mughal India | |
| 1200-2020 | |

|
1200-2020 |
| Policing Untouchables and Producing Tamasha in Maharashtra | |
| 1530-1858 | |

|
1530-1858 |
| Rajputs, Mughals and the Handguns of Hindustan | |
| 1575 | |

|
1575 |
| Abdul Qadir Badauni & Abul Fazl: Two Mughal Intellectuals in King Akbar‘s Court | |
| 1579 | |

|
1579 |
| Padshah-i Islam | |
| 1550-1800 | |

|
1550-1800 |
| Who are the Bengal Muslims? : Conversion and Islamisation in Bengal | |
| c. 1600 CE-1900 CE | |

|
c. 1600 CE-1900 CE |
| The Birth of a Community: UP’s Ghazi Miyan and Narratives of ‘Conquest’ | |
| 1553 - 1900 | |

|
1553 - 1900 |
| What Happened to ‘Hindustan’? | |
| 1630-1680 | |

|
1630-1680 |
| Shivaji: Hindutva Icon or Secular Nationalist? | |
| 1630 -1680 | |

|
1630 -1680 |
| Shivaji: His Legacy & His Times | |
| c. 1724 – 1857 A.D. | |

|
c. 1724 – 1857 A.D. |
| Bahu Begum and the Gendered Struggle for Power | |
| 1818 - Present | |

|
1818 - Present |
| The Contesting Memories of Bhima-Koregaon | |
| 1831 | |

|
1831 |
| The Derozians’ India | |
| 1855 | |

|
1855 |
| Ayodhya 1855 | |
| 1856 | |

|
1856 |
| “Worshipping the dead is not an auspicious thing” — Ghalib | |
| 1857 | |

|
1857 |
| A Subaltern speaks: Dalit women’s counter-history of 1857 | |
| 1858 - 1976 | |

|
1858 - 1976 |
| Lifestyle as Resistance: The Curious Case of the Courtesans of Lucknow | |
| 1883 - 1894 | |

|
1883 - 1894 |
| The Sea Voyage Question: A Nineteenth century Debate | |
| 1887 | |
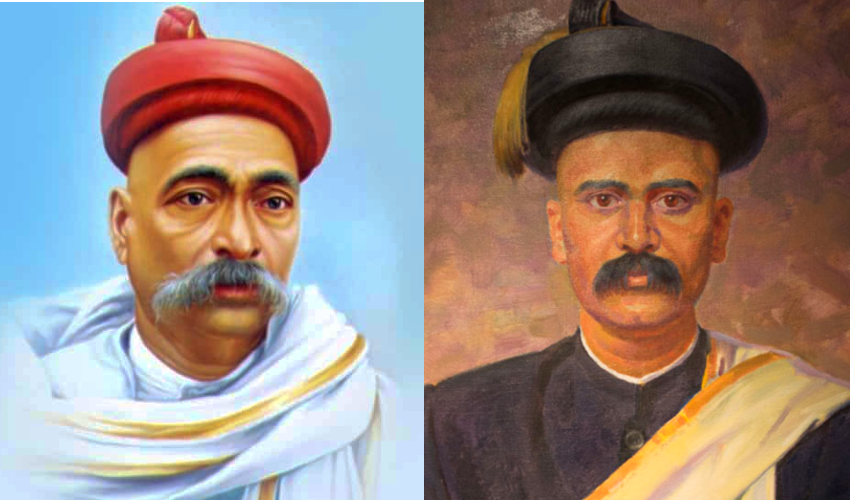

|
1887 |
| The Great Debaters: Tilak Vs. Agarkar | |
| 1893-1946 | |
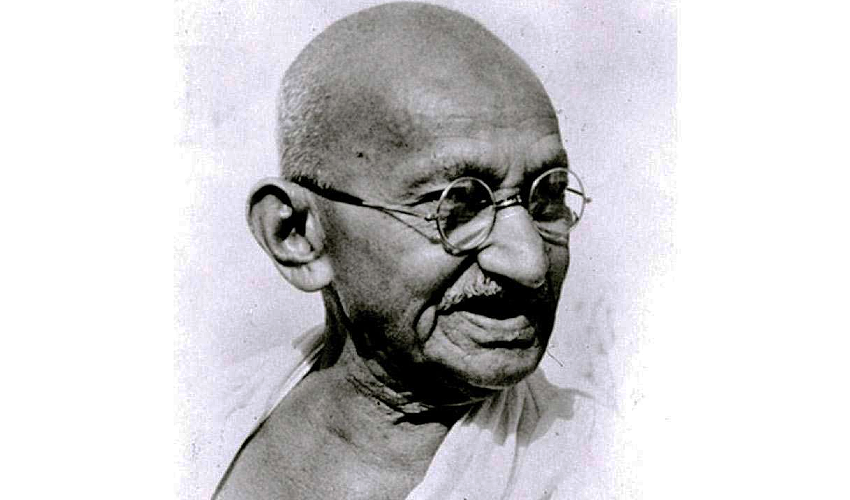

|
1893-1946 |
| A Historian Recommends: Gandhi Vs. Caste | |
| 1897 | |

|
1897 |
| Queen Empress vs. Bal Gangadhar Tilak: An Autopsy | |
| 1913 - 1916 Modern Review | |

|
1913 - 1916 |
| A Young Ambedkar in New York | |
| 1916 | |

|
1916 |
| A Rare Account of World War I by an Indian Soldier | |
| 1917 | |

|
1917 |
| On Nationalism, by Tagore | |
| 1918 - 1919 | |
|
1918 - 1919 |
| What Happened to the Virus That Caused the World’s Deadliest Pandemic? | |
| 1920 - 1947 | |

|
1920 - 1947 |
| How One Should Celebrate Diwali, According to Gandhi | |
| 1921 | |

|
1921 |
| Great Debates: Tagore Vs. Gandhi (1921) | |
| 1921 - 2015 | |

|
1921 - 2015 |
| A History of Caste Politics and Elections in Bihar | |
| 1915-1921 | |

|
1915-1921 |
| The Satirical Genius of Gaganendranath Tagore | |
| 1924-1937 | |
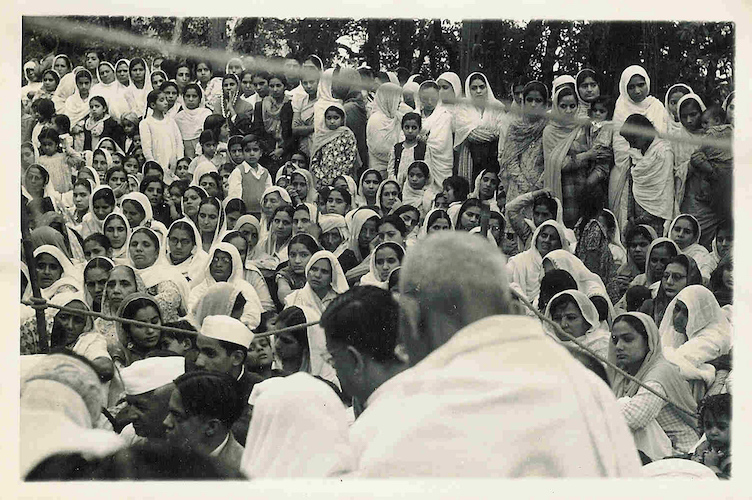

|
1924-1937 |
| What were Gandhi’s Views on Religious Conversion? | |
| 1900-1950 | |

|
1900-1950 |
| Gazing at the Woman’s Body: Historicising Lust and Lechery in a Patriarchal Society | |
| 1925, 1926 | |

|
1925, 1926 |
| Great Debates: Tagore vs Gandhi (1925-1926) | |
| 1928 | |

|
1928 |
| Bhagat Singh’s dilemma: Nehru or Bose? | |
| 1930 Modern Review | |
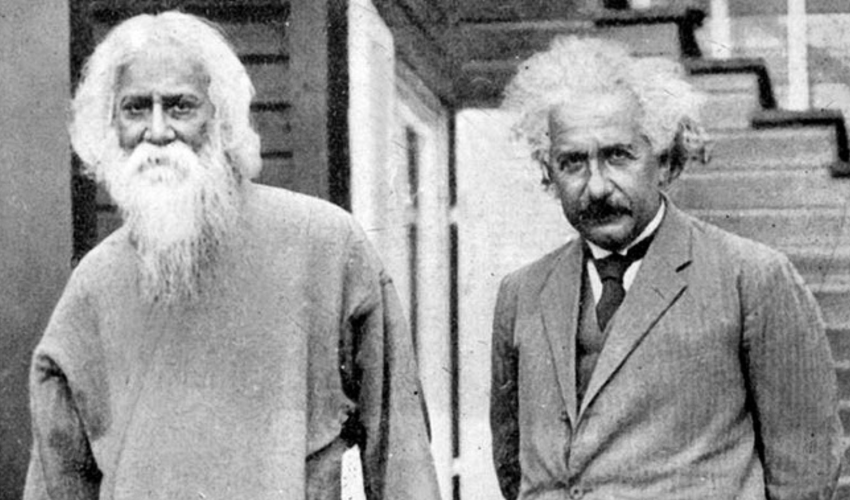

|
1930 |
| The Modern Review Special: On the Nature of Reality | |
| 1932 | |
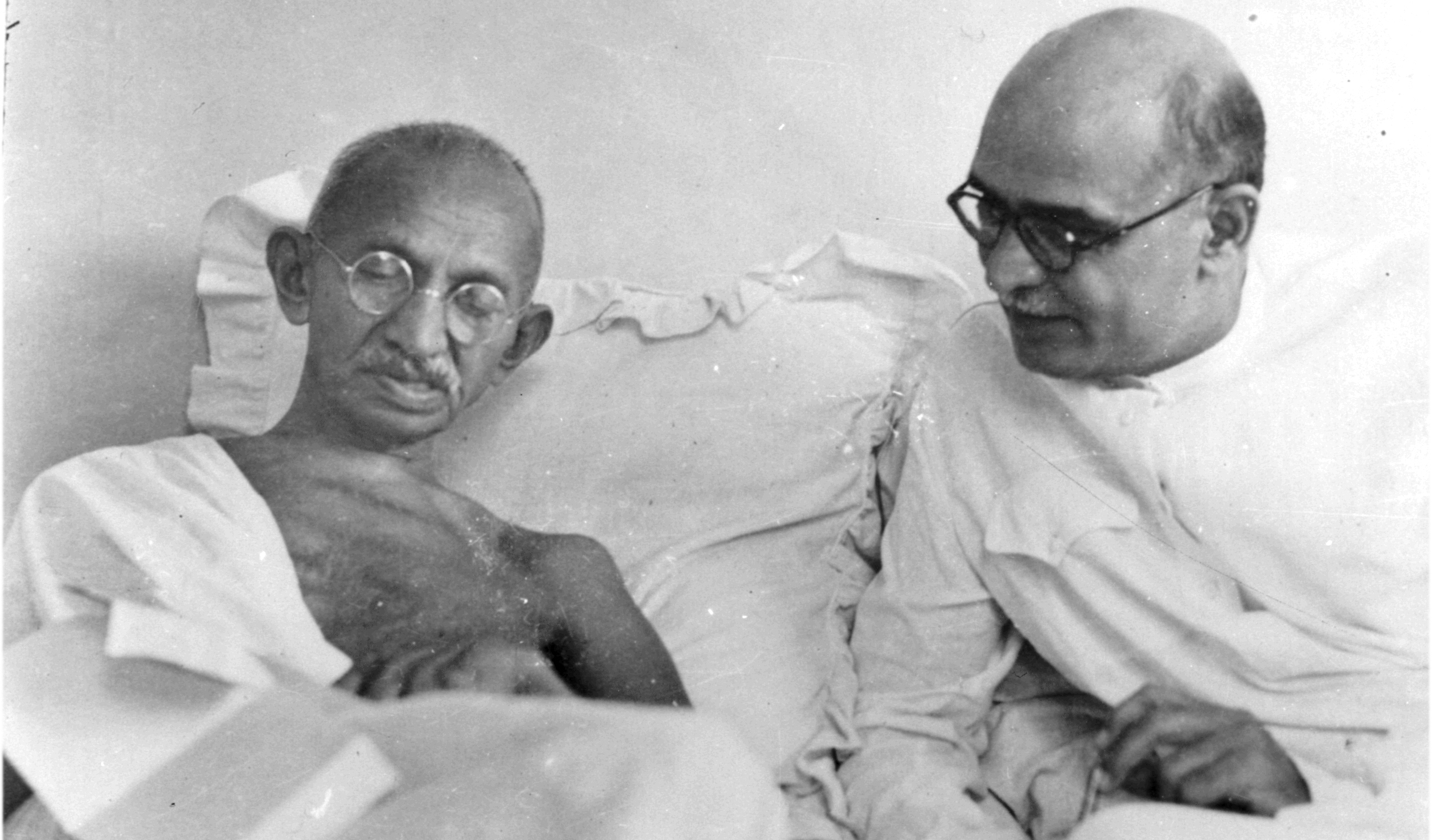

|
1932 |
| Caste, Gandhi and the Man Beside Gandhi | |
| 1933 - 1991 | |

|
1933 - 1991 |
| Raghubir Sinh: The Prince Who Would Be Historian | |
| 1935 | |

|
1935 |
| A Historian Recommends: SA Khan’s Timeless Presidential Address | |
| 1865-1928 | |
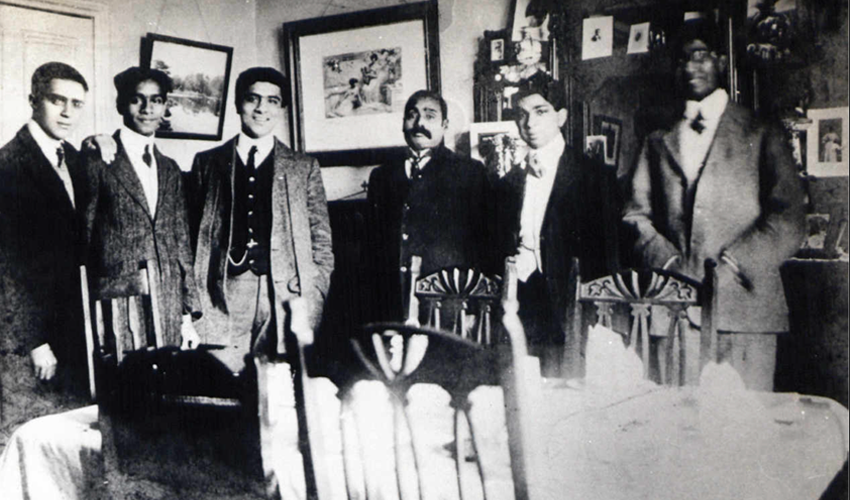

|
1865-1928 |
| Understanding Lajpat Rai’s Hindu Politics and Secularism | |
| 1935 Modern Review | |
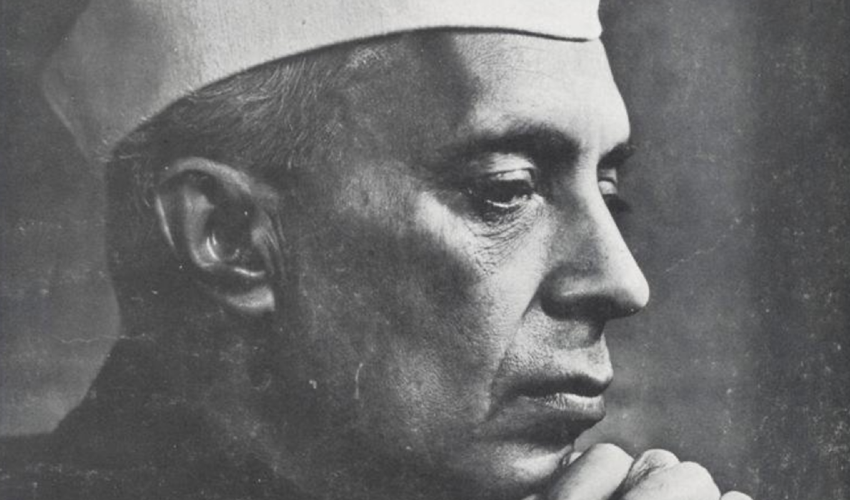

|
1935 |
| The Modern Review Special: The Mind of a Judge | |
| 1936 Modern Review | |
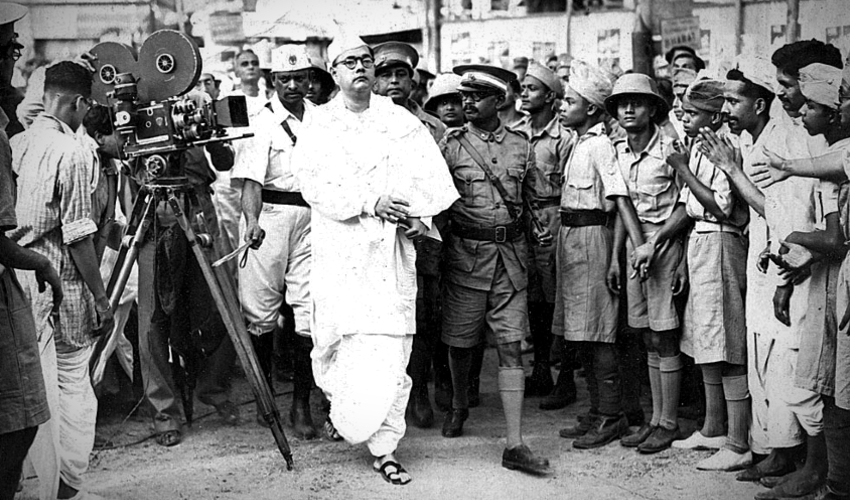

|
1936 |
| The Modern Review Special: When Netaji Subhas Bose Was Wrongfully Detained for ‘Terrorism’ | |
| 1936 | |

|
1936 |
| Annihilation of Caste: Part 1 | |
| 1936 Modern Review | |

|
1936 |
| The Modern Review Special: An Indian MP in the British Parliament | |
| 1936 | |

|
1936 |
| Annihilation of Caste: Part 2 | |
| 1936 | |
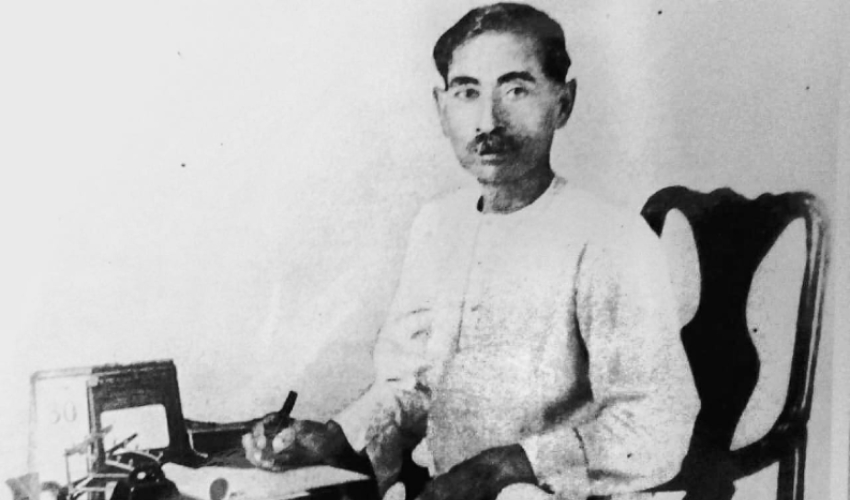

|
1936 |
| A Reflection of His Age: Munshi Premchand on the True Purpose of Literature | |
| 1936 Modern Review | |

|
1936 |
| The Modern Review Special: The Defeat of a Dalit Candidate in a 1936 Municipal Election | |
| 1937 Modern Review | |

|
1937 |
| The Modern Review Special: Rashtrapati | |
| 1938 | |
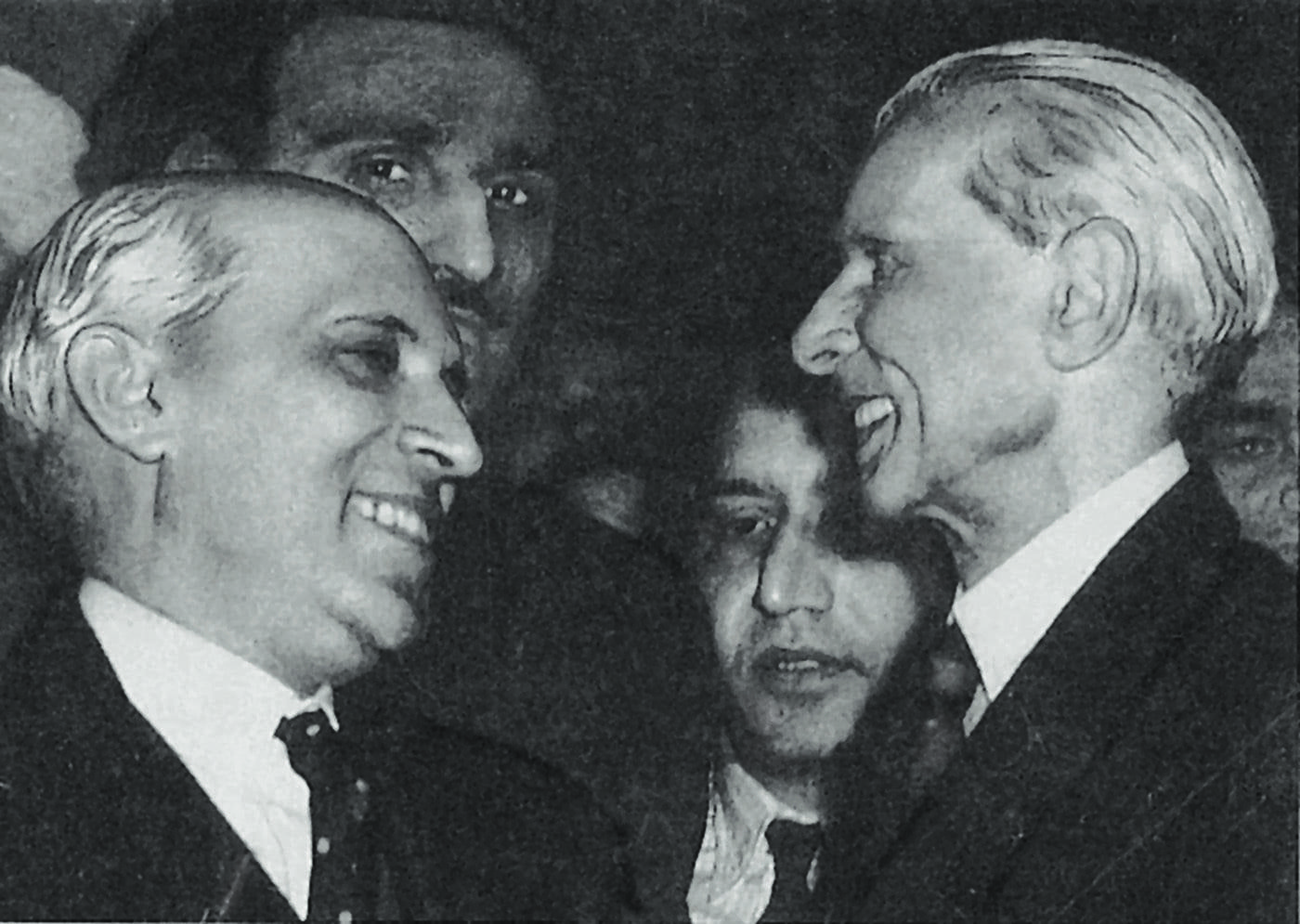

|
1938 |
| Great Debates: Nehru Vs. Jinnah (1938) | |
| 1942 Modern Review | |

|
1942 |
| IHC Uncovers: A Parallel Government In British India (Part 1) | |
| 1942-1945 | |

|
1942-1945 |
| IHC Uncovers: A Parallel Government in British India (Part 2) | |
| 1946 | |

|
1946 |
| Our Last War of Independence: The Royal Indian Navy Mutiny of 1946 | |
| 1946 | |

|
1946 |
| An Artist’s Account of the Tebhaga Movement in Pictures And Prose | |
| 1946 – 1947 | |
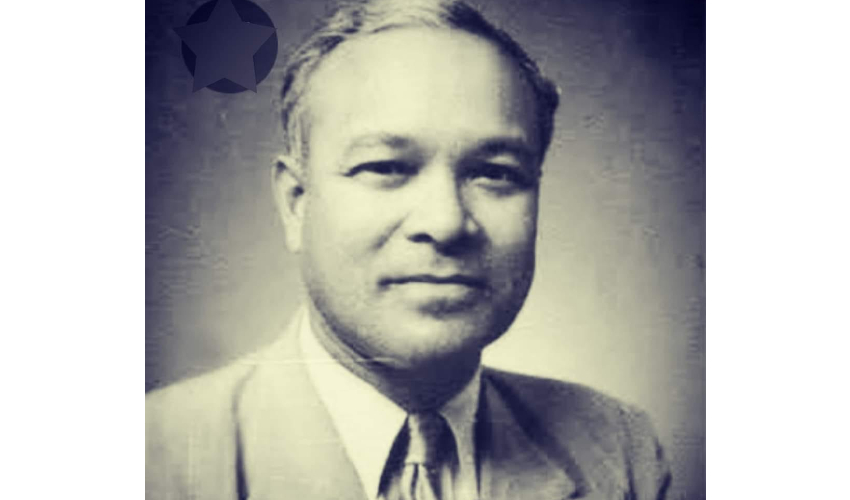

|
1946 – 1947 |
| “The Most Democratic People on Earth” : An Adivasi Voice in the Constituent Assembly | |
| 1946-1947 | |
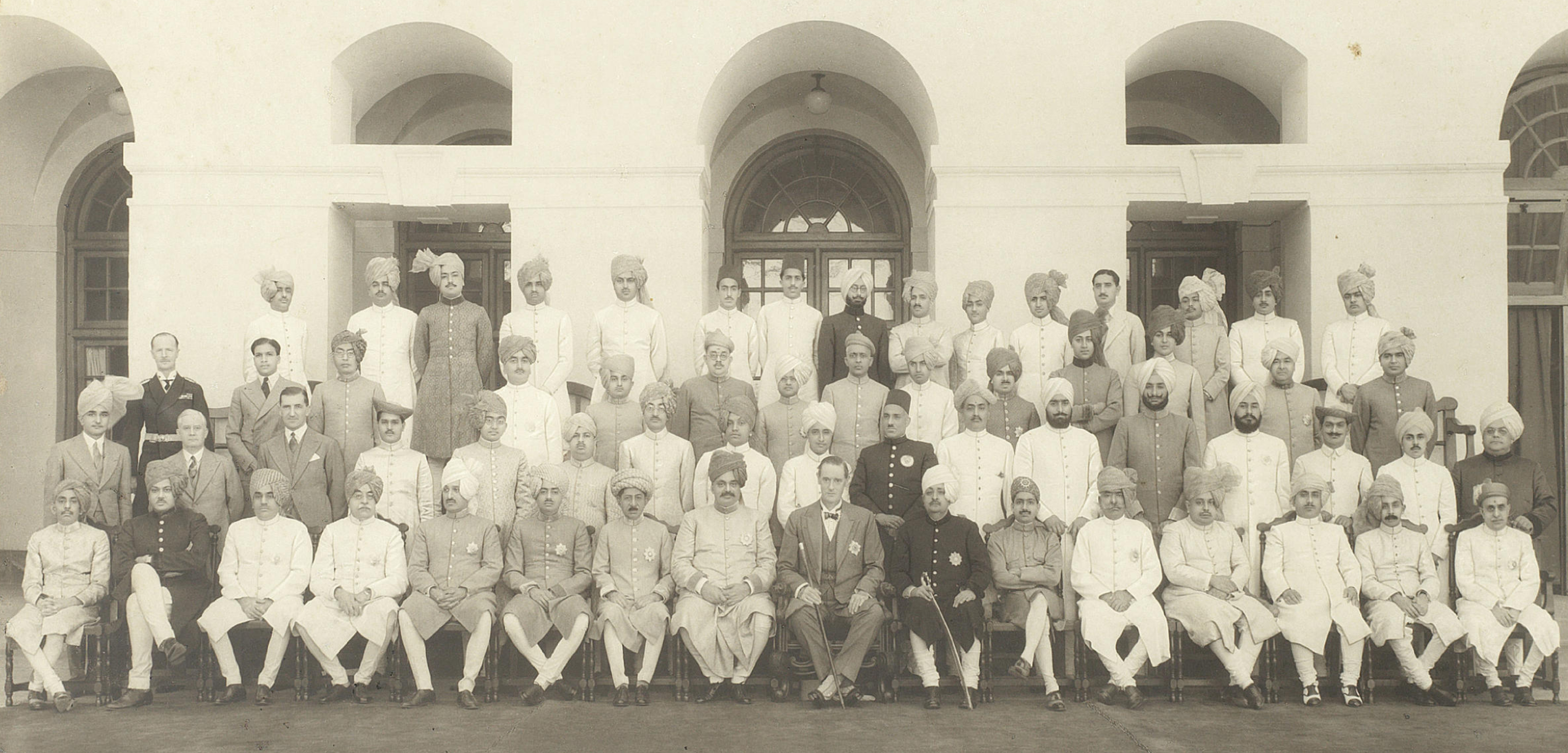

|
1946-1947 |
| VP Menon and the Birth of Independent India | |
| 1916 - 1947 | |

|
1916 - 1947 |
| 8 @ 75: 8 Speeches Independent Indians Must Read | |
| 1947-1951 | |

|
1947-1951 |
| Ambedkar Cartoons: The Joke’s On Us | |
| 1948 | |
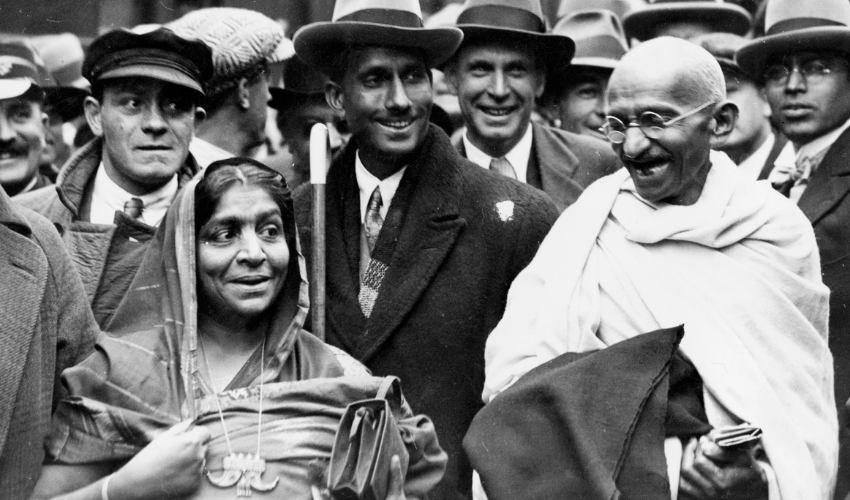

|
1948 |
| “My Father, Do Not Rest” | |
| 1940-1960 | |

|
1940-1960 |
| Integration Myth: A Silenced History of Hyderabad | |
| 1948 | |

|
1948 |
| The Assassination of a Mahatma, the Princely States and the ‘Hindu’ Nation | |
| 1949 | |

|
1949 |
| Ambedkar warns against India becoming a ‘Democracy in Form, Dictatorship in Fact’ | |
| 1950 | |

|
1950 |
| Illustrations from the constitution | |
| 1951 | |
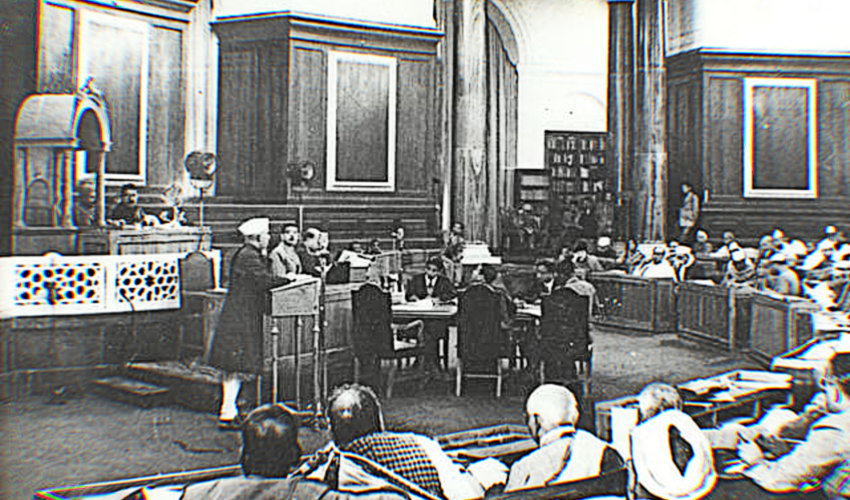

|
1951 |
| How the First Amendment to the Indian Constitution Circumscribed Our Freedoms & How it was Passed | |
| 1967 | |

|
1967 |
| Once Upon A Time In Naxalbari | |
| 1970 | |
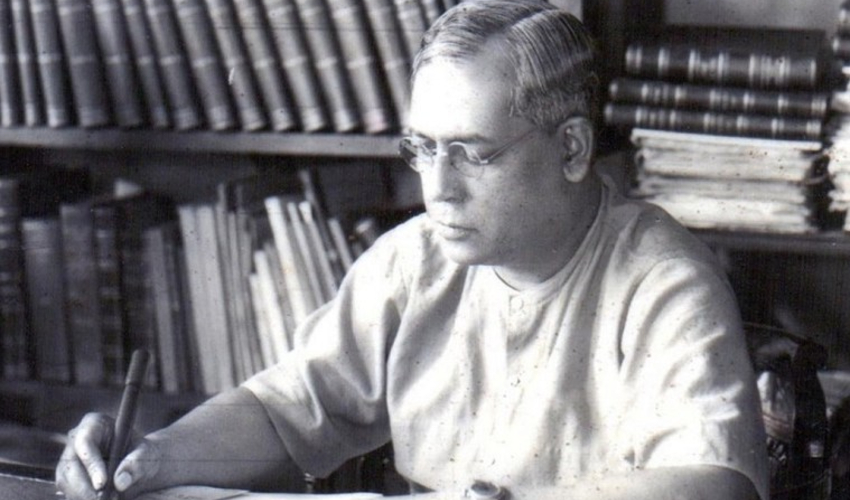

|
1970 |
| R.C. Majumdar on Shortcomings in Indian Historiography | |
| 1973 - 1993 | |

|
1973 - 1993 |
| Balasaheb Deoras: Kingmaker of the Sangh | |
| 1975 | |

|
1975 |
| The Emergency Package: Shadow Power | |
| 1975 | |

|
1975 |
| The Emergency Package: The Prehistory of Turkman Gate – Population Control | |
| 1977 – 2011 | |
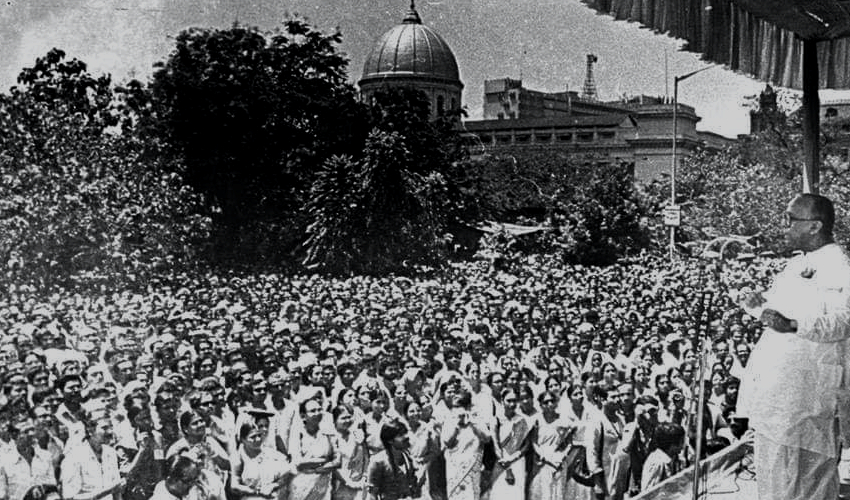

|
1977 – 2011 |
| Power is an Unforgiving Mistress: Lessons from the Decline of the Left in Bengal | |
| 1984 | |

|
1984 |
| Mrs Gandhi’s Final Folly: Operation Blue Star | |
| 1916-2004 | |

|
1916-2004 |
| Amjad Ali Khan on M.S. Subbulakshmi: “A Glorious Chapter for Indian Classical Music” | |
| 2008 | |

|
2008 |
| Whose History Textbook Is It Anyway? | |
| 2006 - 2009 | |

|
2006 - 2009 |
| Singur-Nandigram-Lalgarh: Movements that Remade Mamata Banerjee | |
| 2020 | |

|
2020 |
| The Indo-China Conflict: 10 Books We Need To Read | |
| 2021 | |

|
2021 |
| Singing/Writing Liberation: Dalit Women’s Narratives | |
Leave a Reply